Considerations on brain age predictions from repeatedly sampled data across time
- PMID: 37587620
- PMCID: PMC10570486
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.3219
Considerations on brain age predictions from repeatedly sampled data across time
Abstract
Introduction: Brain age, the estimation of a person's age from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) parameters, has been used as a general indicator of health. The marker requires however further validation for application in clinical contexts. Here, we show how brain age predictions perform for the same individual at various time points and validate our findings with age-matched healthy controls.
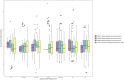
Methods: We used densely sampled T1-weighted MRI data from four individuals (from two densely sampled datasets) to observe how brain age corresponds to age and is influenced by acquisition and quality parameters. For validation, we used two cross-sectional datasets. Brain age was predicted by a pretrained deep learning model.
Results: We found small within-subject correlations between age and brain age. We also found evidence for the influence of field strength on brain age which replicated in the cross-sectional validation data and inconclusive effects of scan quality.
Conclusion: The absence of maturation effects for the age range in the presented sample, brain age model bias (including training age distribution and field strength), and model error are potential reasons for small relationships between age and brain age in densely sampled longitudinal data. Clinical applications of brain age models should consider of the possibility of apparent biases caused by variation in the data acquisition process.
Keywords: T1-weighted; brain age; densely sampled MRI; field strength; magnetic resonance imaging; scan quality.
© 2023 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
O. O. A. has received a speaker's honorarium from Lundbeck and is a consultant to Coretechs.ai.
Figures


References
-
- Beck, D. , Lange, A.‐M. G. , Pedersen, M. L. , Alnæs, D. , Maximov, I. I. , Voldsbekk, I. , Richard, G. , Sanders, A.‐M. , Ulrichsen, K. M. , Dørum, E. S. , Kolskår, K. K. , Høgestøl, E. A. , Steen, N. E. , Djurovic, S. , Andreassen, O. A. , Nordvik, J. E. , Kaufmann, T. , & Westlye, L. T. (2022). Cardiometabolic risk factors associated with brain age and accelerate brain ageing. Human Brain Mapping, 43(2), 700–720. 10.1002/hbm.25680 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dörfel, R. P. , Arenas‐Gomez, J. M. , Fisher, P. M. , Ganz, M. , Knudsen, G. M. , Svensson, J. , & Plaven‐Sigray, P. (2023). Prediction of brain age using structural magnetic resonance imaging: A comparison of accuracy and test‐retest reliability of publicly available software packages. BioRxiv, 2023–01. 10.1101/2023.01.26.525514 bioRxiv - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

