Design, synthesis and evaluation of dihydro-1 H-indene derivatives as novel tubulin polymerisation inhibitors with anti-angiogenic and antitumor potency
- PMID: 37587873
- PMCID: PMC10438863
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2247579
Design, synthesis and evaluation of dihydro-1 H-indene derivatives as novel tubulin polymerisation inhibitors with anti-angiogenic and antitumor potency
Abstract
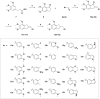
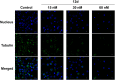
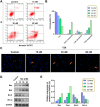
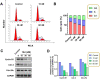
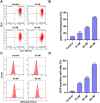
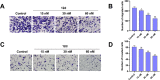
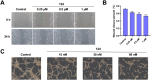
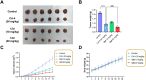
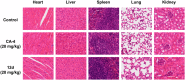
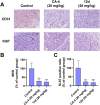
Angiogenesis plays an important role in tumour generation and progression, which is used to supply nutrients and metastasis. Herein, a series of novel dihydro-1H-indene derivatives were designed and evaluated as tubulin polymerisation inhibitors by binding to colchicine site, exhibiting anti-angiogenic activities against new vessel forming. Through structure-activity relationships study, compound 12d was found to be the most potent derivative possessing the antiproliferative activity against four cancer lines with IC50 values among 0.028-0.087 µM. Compound 12d bound to colchicine site on tubulin and inhibited tubulin polymerisation in vitro. In addition, compound 12d induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase, stimulated cell apoptosis, inhibited tumour metastasis and angiogenesis. Finally, the results of in vivo assay suggested that compound 12d could prevent tumour generation, inhibit tumour proliferation and angiogenesis without obvious toxicity. Collectively, all these findings suggested that compound 12d is a novel tubulin polymerisation inhibitor deserving further research.
Keywords: Anticancer; angiogenesis; colchicine binding site; indene; tubulin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


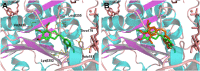
References
-
- Jordan MA, Wilson L.. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(4):253–265. - PubMed
-
- Penna LS, Henriques JAP, Bonatto D.. Anti-mitotic agents: are they emerging molecules for cancer treatment? Pharmacol Ther. 2017;173:67–82. - PubMed
-
- Islam MN, Iskander MN.. Microtubulin binding sites as target for developing anticancer agents. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2004;4(10):1077–1104. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
