Novel or established cryoballoon ablation system for pulmonary vein isolation: the prospective ICE-AGE-1 study
- PMID: 37589146
- PMCID: PMC10468200
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euad248
Novel or established cryoballoon ablation system for pulmonary vein isolation: the prospective ICE-AGE-1 study
Abstract
Aims: Catheter ablation with a cryoballoon (CB) provides effective and durable pulmonary vein (PV) isolation (PVI) associated with encouraging clinical outcome data. The novel POLARx CB incorporates unique features, which may translate into improved safety, efficacy, and outcomes. The ICE-AGE-1 study aimed to assess the efficacy, safety, and 1-year clinical follow-up of the POLARx CB in comparison to the Arctic Front Advance Pro CB (AF-CB4).
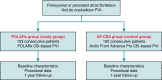
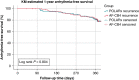
Methods and results: A total of 103 consecutive patients with paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) who underwent POLARx-based PVI (POLARx group) were prospectively enrolled and were compared to 102 consecutive patients previously treated with the AF-CB4 (AF-CB4 group). The mean age was 68.7 ± 10.2 (POLARx) and 65.7 ± 12 (AF-CB4, P = 0.0551) years. A total of 412 (POLARx) and 404 (AF-CB4) PVs were identified. All PVs, except for one PV in the POLARx group, were successfully isolated. A significant difference regarding the mean minimal CB temperature reached using the POLARx CB (-56.1 ± 8.3°C) and AF-CB4 (-46.9 ± 10.1°C) was observed (P < 0.0001). Real-time PVI was visualized in 71% of PVs in the POLARx group and 46% of them in the AF-CB4 group (P < 0.001). The mean procedure time was comparable: 54.5 ± 17.1 min for POLARx and 59.4 ± 18.6 min for AF-CB4 (P = 0.0509). No differences were observed in terms of periprocedural complications. There were comparable rates in freedom of AF or atrial tachycardia recurrence after 12 months, beyond a 90-day long blanking period: 78.9% in the POLARx group vs. 77.2% in the AF-CB4 group (P = 0.804).
Conclusion: The novel POLARx CB showed similar safety, efficacy, and 1-year recurrence-free survival rates compared to the AF-CB4. A higher rate of real-time electrical PV recordings and significantly lower balloon temperatures were observed using the POLARx as compared to AF-CB4.
Keywords: Acute efficacy; Atrial fibrillation; Cryoballoon; Follow-up; Pulmonary vein isolation.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
References
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist Cet al. . 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J 2021;42:373–498. - PubMed
-
- Sørensen SK, Johannessen A, Worck R, Hansen ML, Hansen J. Radiofrequency versus cryoballoon catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: durability of pulmonary vein isolation and effect on atrial fibrillation burden: the RACE-AF randomized controlled trial. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2021;14. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrade JG, Champagne J, Dubuc M, Deyell MW, Verma A, Macle Let al. . Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation assessed by continuous monitoring. Circulation 2019;140:1779–88. - PubMed
-
- Kuck KH, Brugada J, Fürnkranz A, Metzner A, Ouyang F, Chun KRJet al. . Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2016;374:2235–45. - PubMed
-
- Ciconte G, Ottaviano L, de Asmundis C, Baltogiannis G, Conte G, Sieira Jet al. . Pulmonary vein isolation as index procedure for persistent atrial fibrillation: one-year clinical outcome after ablation using the second-generation cryoballoon. Heart Rhythm 2015;12:60–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

