Empowering canonical biochemicals with cross-linked novelty: Recursions in applications of protein cross-links
- PMID: 37589191
- PMCID: PMC7616502
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.26571
Empowering canonical biochemicals with cross-linked novelty: Recursions in applications of protein cross-links
Abstract
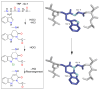
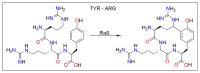
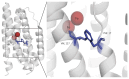
Diversity in the biochemical workhorses of the cell-that is, proteins-is achieved by the innumerable permutations offered primarily by the 20 canonical L-amino acids prevalent in all biological systems. Yet, proteins are known to additionally undergo unusual modifications for specialized functions. Of the various post-translational modifications known to occur in proteins, the recently identified non-disulfide cross-links are unique, residue-specific covalent modifications that confer additional structural stability and unique functional characteristics to these biomolecules. We review an exclusive class of amino acid cross-links encompassing aromatic and sulfur-containing side chains, which not only confer superior biochemical characteristics to the protein but also possess additional spectroscopic features that can be exploited as novel chromophores. Studies of their in vivo reaction mechanism have facilitated their specialized in vitro applications in hydrogels and protein anchoring in monolayer chips. Furthering the discovery of unique canonical cross-links through new chemical, structural, and bioinformatics tools will catalyze the development of protein-specific hyperstable nanostructures, superfoods, and biotherapeutics.
Keywords: hyperstable structures; novel protein function; side chain modification; unusual cross‐link.
© 2023 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

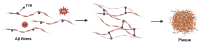





References
-
- Lee D, Redfern O, Orengo C. Predicting protein function from sequence and structure. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(12):995–1005. - PubMed
-
- Dill KA, MacCallum JL. The protein-folding problem, 50 years on. Science. 2012;338(6110):1042–1046. - PubMed
-
- Kahn A, Boivin P, Rubinson H, Cottreau D, Marie J, Dreyfus JC. Modifications of purified glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and other enzymes by a factor of low molecular weight abundant in some leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976;73(1):77–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.77. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kivirikko KI, Risteli L. Biosynthesis of collagen and its alterations in pathological states. Med Biol. 1976;54(3):159–186. - PubMed
-
- Risteli J, Kivirikko KI. Intracellular enzymes of collagen biosynthesis in rat liver as a function of age and in hepatic injury induced by dimethylnitrosamine. Changes in prolyl hydroxylase, lysyl hydroxylase, collagen galactosyltransferase and collagen glucosyltransferase activities. Biochem J. 1976;158(2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj1580361. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- IA/S/20/2/505182/WTDBT_/DBT-Wellcome Trust India Alliance/India
- BT/PR28858/BRB/10/1718/2018/Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, India
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- IA/S/20/2/505182/The Wellcome Trust DBT India Alliance
- SPR/2021/000018/Science and Engineering Research Board
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

