Beyond skin-deep: targeting the plant surface for crop improvement
- PMID: 37589495
- PMCID: PMC10662250
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erad321
Beyond skin-deep: targeting the plant surface for crop improvement
Abstract
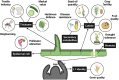
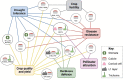
The above-ground plant surface is a well-adapted tissue layer that acts as an interface between the plant and its surrounding environment. As such, its primary role is to protect against desiccation and maintain the gaseous exchange required for photosynthesis. Further, this surface layer provides a barrier against pathogens and herbivory, while attracting pollinators and agents of seed dispersal. In the context of agriculture, the plant surface is strongly linked to post-harvest crop quality and yield. The epidermal layer contains several unique cell types adapted for these functions, while the non-lignified above-ground plant organs are covered by a hydrophobic cuticular membrane. This review aims to provide an overview of the latest understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying crop cuticle and epidermal cell formation, with focus placed on genetic elements contributing towards quality, yield, drought tolerance, herbivory defence, pathogen resistance, pollinator attraction, and sterility, while highlighting the inter-relatedness of plant surface development and traits. Potential crop improvement strategies utilizing this knowledge are outlined in the context of the recent development of new breeding techniques.
Keywords: Biotechnology; crop improvement; cuticle; drought tolerance; epidermal layer; fruit quality; new breeding techniques (NBTs); stomata; trichome.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest declared.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmad S, Tang L, Shahzad R, et al. 2021. CRISPR-based crop improvements: a way forward to achieve zero hunger. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 69, 8307–8323. - PubMed
-
- An X, Dong Z, Tian Y, et al. 2019. ZmMs30 encoding a novel GDSL lipase is essential for male fertility and valuable for hybrid breeding in maize. Molecular Plant 12, 343–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

