Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis: Recent Advances
- PMID: 37589918
- PMCID: PMC10468923
- DOI: 10.1007/s11910-023-01290-2
Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis: Recent Advances
Abstract
Purpose of review: Autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) is increasingly considered a treatment option for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune demyelinating and degenerative disease of the central nervous system (CNS). AHSCT persistently suppresses inflammation and improves the disease course in large proportions of patients with relapsing-remitting (RR) MS. Aim of this article is to review the relevant new knowledge published during the last 3 years.
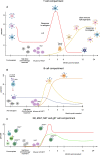
Recent findings: Laboratory studies reported confirmatory and new insights into the immunological and biomarker effects of AHSCT. Retrospective clinical studies confirmed excellent outcomes in RRMS, showing possible superior effectiveness over standard therapies and suggesting a possible benefit in early secondary progressive (SP) MS with inflammatory features. New data on risks of infertility and secondary autoimmunity were also reported. Further evidence on the high effectiveness and acceptable safety of AHSCT strengthens its position as a clinical option for aggressive RRMS. Further research is needed to better define its role in treatment-naïve and progressive forms of MS, ideally within randomised clinical trials (RCTs).
Keywords: Alemtuzumab; Biomarker; Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Multiple sclerosis; Reconstitution.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Mariottini reports personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Biogen, non-financial support from Sanofi, non-financial support from Biogen, non-financial support from Janssen Neuroscience and non-financial support from Merck, outside the submitted work. Dr. De Matteis has nothing to disclose. Dr. Cencioni has nothing to disclose. Prof. Muraro reports grants from National Institute of Health Research, non-financial support from National Institute of Health Research and grants from Benaroya Research Institute and National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health, during the conduct of the study, and personal fees from Jasper Therapeutics, personal fees from Magenta Therapeutics, personal fees from Quell Therapeutics and personal fees from Rubius Therapeutics, outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Cencioni MT, Genchi A, Brittain G, de Silva TI, Sharrack B, Snowden JA, et al. Immune reconstitution following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for multiple sclerosis: a review on behalf of the EBMT Autoimmune Diseases Working Party. Front Immunol. 2021;12:813957. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.813957. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharrack B, Saccardi R, Alexander T, Badoglio M, Burman J, Farge D, et al. Autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation and other cellular therapy in multiple sclerosis and immune-mediated neurological diseases: updated guidelines and recommendations from the EBMT Autoimmune Diseases Working Party (ADWP) and the Joint Accreditation Committee of EBMT and ISCT (JACIE) Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0684-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohen JA, Baldassari LE, Atkins HL, Bowen JD, Bredeson C, Carpenter PA, et al. Autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for treatment-refractory relapsing multiple sclerosis: position statement from the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25(5):845–854. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.02.014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

