Long-Term Clinical Outcomes of Single Crowns or Short Fixed Partial Dentures Supported by Short (≤6 mm) Dental Implants: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37591286
- PMCID: PMC10959620
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1771028
Long-Term Clinical Outcomes of Single Crowns or Short Fixed Partial Dentures Supported by Short (≤6 mm) Dental Implants: A Systematic Review
Abstract
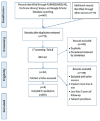
Long-term clinical outcomes of short dental implants (≤6 mm) supporting single crowns or short fixed partial dentures have been reported differently in different studies and need more clarification. This systematic study evaluated the rate of bone loss (BL), the durability of implants equal to or shorter than 6 mm supporting single crowns or short fixed partial dentures, and prosthetic-related side effects during 5 years of follow-up. Five databases (PubMed, MEDLINE, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Cochrane) were electronically and manually searched for longitudinal studies with a follow-up period of 5 years or more until January 2023. The study question was, "Does the implant equal to or shorter than 6 mm affect BL and survival rate of the implant-supported prosthesis after 5 years of follow-up?". From 752 identified articles, nine studies were selected for further evaluation. After 5 years of follow-up, most studies had more than 90% survival rate and the maximum BL was 0.54 mm. Still, in internal and external connections, these changes were not substantial. For example, screw loosening was the most common problem with implanted prostheses. Implants of 6 mm or shorter are a suitable treatment option in atrophic ridges with good durability and fewer side effects during a follow-up period of more than 5 years.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared
Figures
References
-
- Naert I, Quirynen M, van Steenberghe D, Darius P. A six-year prosthodontic study of 509 consecutively inserted implants for the treatment of partial edentulism. J Prosthet Dent. 1992;67(02):236–245. - PubMed
-
- Urban I A, Jovanovic S A, Lozada J L. Vertical ridge augmentation using guided bone regeneration (GBR) in three clinical scenarios prior to implant placement: a retrospective study of 35 patients 12 to 72 months after loading. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(03):502–510. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz-Arad D, Ofec R, Eliyahu G, Ruban A, Sterer N. Long term follow-up of dental implants placed in autologous Onlay bone graft. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2016;18(03):449–461. - PubMed
-
- Fontana F, Maschera E, Rocchietta I, Simion M. Clinical classification of complications in guided bone regeneration procedures by means of a nonresorbable membrane. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2011;31(03):265–273. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources