Auxin and abiotic stress responses
- PMID: 37591508
- PMCID: PMC10690732
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erad325
Auxin and abiotic stress responses
Abstract
Plants are exposed to a variety of abiotic stresses; these stresses have profound effects on plant growth, survival, and productivity. Tolerance and adaptation to stress require sophisticated stress sensing, signaling, and various regulatory mechanisms. The plant hormone auxin is a key regulator of plant growth and development, playing pivotal roles in the integration of abiotic stress signals and control of downstream stress responses. In this review, we summarize and discuss recent advances in understanding the intersection of auxin and abiotic stress in plants, with a focus on temperature, salt, and drought stresses. We also explore the roles of auxin in stress tolerance and opportunities arising for agricultural applications.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; auxin; drought; phytohormone; salt; temperature.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
LCS is on the Science Advisory Board for Prose Foods.
Figures
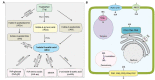
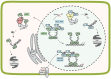
References
-
- Abeysingha DN, Ozga JA, Strydhorst S, Doyle P, Iqbal M, Yang R-C, Reinecke DM.. 2021. The effect of auxins on amelioration of heat stress-induced wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain loss. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science 207, 970–983.
-
- Ashraf MA, Rahman A.. 2019. Cold stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana is mediated by GNOM ARF-GEF. The Plant Journal 97, 500–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

