Marshalling the Potential of Auger Electron Radiopharmaceutical Therapy
- PMID: 37591544
- PMCID: PMC10478825
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.122.265039
Marshalling the Potential of Auger Electron Radiopharmaceutical Therapy
Abstract
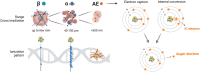
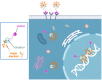
Auger electron (AE) radiopharmaceutical therapy (RPT) may have the same therapeutic efficacy as α-particles for oncologic small disease, with lower risks of normal-tissue toxicity. The seeds of using AE emitters for RPT were planted several decades ago. Much knowledge has been gathered about the potency of the biologic effects caused by the intense shower of these low-energy AEs. Given their short range, AEs deposit much of their energy in the immediate vicinity of their site of decay. However, the promise of AE RPT has not yet been realized, with few agents evaluated in clinical trials and none becoming part of routine treatment so far. Instigated by the 2022 "Technical Meeting on Auger Electron Emitters for Radiopharmaceutical Developments" at the International Atomic Energy Agency, this review presents the current status of AE RPT based on the discussions by experts in the field. A scoring system was applied to illustrate hurdles in the development of AE RPT, and we present a selected list of well-studied and emerging AE-emitting radionuclides. Based on the number of AEs and other emissions, physical half-life, radionuclide production, radiochemical approaches, dosimetry, and vector availability, recommendations are put forward to enhance and impact future efforts in AE RPT research.
Keywords: Auger electrons emitters; radiopharmaceutical therapy; radiopharmaceuticals; recommendations.
© 2023 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures


References
-
- Howell RW. Radiation spectra for Auger-electron emitting radionuclides: report no. 2 of AAPM Nuclear Medicine Task Group No. 6. Med Phys. 1992;19:1371–1383. - PubMed
-
- Kassis AI, Sastry KS, Adelstein SJ. Kinetics of uptake, retention, and radiotoxicity of 125IUdR in mammalian cells: implications of localized energy deposition by Auger processes. Radiat Res. 1987;109:78–89. - PubMed
-
- Kassis AI, Fayad F, Kinsey BM, Sastry KS, Adelstein SJ. Radiotoxicity of an 125I-labeled DNA intercalator in mammalian cells. Radiat Res. 1989;118:283–294. - PubMed
-
- Pouget JP, Santoro L, Raymond L, et al. . Cell membrane is a more sensitive target than cytoplasm to dense ionization produced by Auger electrons. Radiat Res. 2008;170:192–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
