Immune defenses in the urinary tract
- PMID: 37591712
- PMCID: PMC10528756
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2023.07.001
Immune defenses in the urinary tract
Abstract
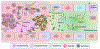
Recent advances in preclinical modeling of urinary tract infections (UTIs) have enabled the identification of key facets of the host response that influence pathogen clearance and tissue damage. Here, we review new insights into the functions of neutrophils, macrophages, and antimicrobial peptides in innate control of uropathogens and in mammalian infection-related tissue injury and repair. We also discuss novel functions for renal epithelial cells in innate antimicrobial defense. In addition, epigenetic modifications during bacterial cystitis have been implicated in bladder remodeling, conveying susceptibility to recurrent UTI. In total, contemporary work in this arena has better defined host processes that shape UTI susceptibility and severity and might inform the development of novel preventive and therapeutic approaches for acute and recurrent UTI.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; antimicrobial peptides; epigenetic remodeling; innate immunity; macrophages; neutrophils; pyelonephritis.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.A.H. serves on the Board of Directors of BioVersys AG, Basel, Switzerland, and has received research funding from BioAge Labs, Richmond, CA, USA. These activities are unrelated to the content of this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amplifying renal immunity: the role of antimicrobial peptides in pyelonephritis.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015 Nov;11(11):642-55. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.105. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26149835 Review.
-
Host-Derived Nitric Oxide and Its Antibacterial Effects in the Urinary Tract.Adv Microb Physiol. 2018;73:1-62. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Adv Microb Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30262107
-
Innate immunity and urinary tract infection.Pediatr Nephrol. 2020 Jul;35(7):1183-1192. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04269-9. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Pediatr Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31197473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Augmentation of Urinary Lactoferrin Enhances Host Innate Immune Clearance of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.J Innate Immun. 2019;11(6):481-495. doi: 10.1159/000499342. Epub 2019 May 3. J Innate Immun. 2019. PMID: 31055580 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary tract infections in women.Can J Urol. 2001 Jun;8 Suppl 1:6-12. Can J Urol. 2001. PMID: 11442991 Review.
Cited by
-
Murine Ribonuclease 6 Limits Bacterial Dissemination during Experimental Urinary Tract Infection.J Innate Immun. 2024;16(1):283-294. doi: 10.1159/000539177. Epub 2024 May 14. J Innate Immun. 2024. PMID: 38744252 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of immune and diagnostic biomarkers for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome by integrating bioinformatics and machine-learning.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 23;16:1511529. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1511529. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39917301 Free PMC article.
-
Current and emerging strategies to curb antibiotic-resistant urinary tract infections.Nat Rev Urol. 2024 Dec;21(12):707-722. doi: 10.1038/s41585-024-00877-9. Epub 2024 May 7. Nat Rev Urol. 2024. PMID: 38714857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Common Polymorphism in RNASE6 Impacts Its Antimicrobial Activity toward Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 3;25(1):604. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010604. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203775 Free PMC article.
-
Role of N-acetylkynurenine in mediating the effect of gut microbiota on urinary tract infection: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 22;15:1384095. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1384095. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38711967 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

