Application of artificial intelligence in endoscopic image analysis for the diagnosis of a gastric cancer pathogen-Helicobacter pylori infection
- PMID: 37592004
- PMCID: PMC10435453
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-40179-5
Application of artificial intelligence in endoscopic image analysis for the diagnosis of a gastric cancer pathogen-Helicobacter pylori infection
Abstract
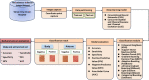
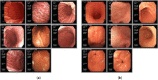
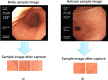
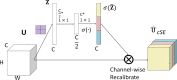
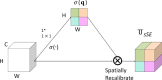
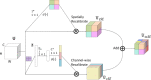
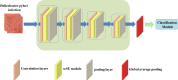
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is the principal cause of chronic gastritis, gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers, and gastric cancer. In clinical practice, diagnosis of H. pylori infection by a gastroenterologists' impression of endoscopic images is inaccurate and cannot be used for the management of gastrointestinal diseases. The aim of this study was to develop an artificial intelligence classification system for the diagnosis of H. pylori infection by pre-processing endoscopic images and machine learning methods. Endoscopic images of the gastric body and antrum from 302 patients receiving endoscopy with confirmation of H. pylori status by a rapid urease test at An Nan Hospital were obtained for the derivation and validation of an artificial intelligence classification system. The H. pylori status was interpreted as positive or negative by Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Concurrent Spatial and Channel Squeeze and Excitation (scSE) network, combined with different classification models for deep learning of gastric images. The comprehensive assessment for H. pylori status by scSE-CatBoost classification models for both body and antrum images from same patients achieved an accuracy of 0.90, sensitivity of 1.00, specificity of 0.81, positive predictive value of 0.82, negative predicted value of 1.00, and area under the curve of 0.88. The data suggest that an artificial intelligence classification model using scSE-CatBoost deep learning for gastric endoscopic images can distinguish H. pylori status with good performance and is useful for the survey or diagnosis of H. pylori infection in clinical practice.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

