Molecular docking as a tool for the discovery of molecular targets of nutraceuticals in diseases management
- PMID: 37592012
- PMCID: PMC10435576
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-40160-2
Molecular docking as a tool for the discovery of molecular targets of nutraceuticals in diseases management
Abstract
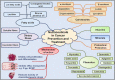
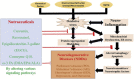
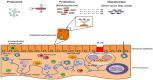
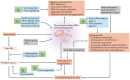
Molecular docking is a computational technique that predicts the binding affinity of ligands to receptor proteins. Although it has potential uses in nutraceutical research, it has developed into a formidable tool for drug development. Bioactive substances called nutraceuticals are present in food sources and can be used in the management of diseases. Finding their molecular targets can help in the creation of disease-specific new therapies. The purpose of this review was to explore molecular docking's application to the study of dietary supplements and disease management. First, an overview of the fundamentals of molecular docking and the various software tools available for docking was presented. The limitations and difficulties of using molecular docking in nutraceutical research are also covered, including the reliability of scoring functions and the requirement for experimental validation. Additionally, there was a focus on the identification of molecular targets for nutraceuticals in numerous disease models, including those for sickle cell disease, cancer, cardiovascular, gut, reproductive, and neurodegenerative disorders. We further highlighted biochemistry pathways and models from recent studies that have revealed molecular mechanisms to pinpoint new nutraceuticals' effects on disease pathogenesis. It is convincingly true that molecular docking is a useful tool for identifying the molecular targets of nutraceuticals in the management of diseases. It may offer information about how nutraceuticals work and support the creation of new therapeutics. Therefore, molecular docking has a bright future in nutraceutical research and has a lot of potentials to lead to the creation of brand-new medicines for the treatment of disease.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of Nutraceuticals in Obesity Management: A Mechanism and Prospective Supported by Molecular Docking Studies.J Med Food. 2024 Feb;27(2):176-197. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2023.0104. Epub 2024 Feb 6. J Med Food. 2024. PMID: 38324003
-
A Comprehensive Review on Nutraceuticals: Therapy Support and Formulation Challenges.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 3;14(21):4637. doi: 10.3390/nu14214637. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational strategies for the discovery of biological functions of health foods, nutraceuticals and cosmeceuticals: a review.Mol Divers. 2021 Aug;25(3):1425-1438. doi: 10.1007/s11030-021-10277-5. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Mol Divers. 2021. PMID: 34258685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining 'nutraceuticals': neither nutritious nor pharmaceutical.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;83(1):8-19. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12935. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 26991455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Prospects of Nutraceuticals: A Review.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020;21(10):884-896. doi: 10.2174/1389201021666200130113441. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32000642 Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Drug Repurposing Endorse Amprenavir, Darunavir and Saquinavir to Target Enzymes of Multidrug Resistant Uropathogenic E. Coli.Indian J Microbiol. 2024 Sep;64(3):1153-1214. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01282-x. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Indian J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39282172
-
Newly discovered clouting interplay between matrix metalloproteinases structures and novel quaternary Ammonium K21: computational and in-vivo testing.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Mar 25;24(1):382. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04069-0. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38528501 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS profiling and cytotoxic activity of Angiopteris helferiana against HepG2 cell line: Molecular insight to investigate anticancer agent.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 31;19(12):e0309797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309797. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39739862 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Investigation of Montelukast and Its Structural Derivatives for Binding Affinity to Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Receptors: Insights from a Comprehensive Molecular Simulation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 10;18(4):559. doi: 10.3390/ph18040559. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283994 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Validation to Explore the Effects and Mechanisms of Indirubin on Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Feb 18;19:1083-1103. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S500249. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39991083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sahoo RN, Pattanaik S, Pattnaik G, Mallick S, Mohapatra R. Review on the use of molecular docking as the first line tool in drug discovery and development. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022;84(5):1334–1337.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

