Intrinsically disordered domain of transcription factor TCF-1 is required for T cell developmental fidelity
- PMID: 37592014
- PMCID: PMC10919931
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-023-01599-7
Intrinsically disordered domain of transcription factor TCF-1 is required for T cell developmental fidelity
Abstract
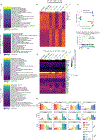
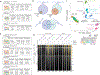
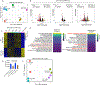
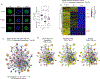
In development, pioneer transcription factors access silent chromatin to reveal lineage-specific gene programs. The structured DNA-binding domains of pioneer factors have been well characterized, but whether and how intrinsically disordered regions affect chromatin and control cell fate is unclear. Here, we report that deletion of an intrinsically disordered region of the pioneer factor TCF-1 (termed L1) leads to an early developmental block in T cells. The few T cells that develop from progenitors expressing TCF-1 lacking L1 exhibit lineage infidelity distinct from the lineage diversion of TCF-1-deficient cells. Mechanistically, L1 is required for activation of T cell genes and repression of GATA2-driven genes, normally reserved to the mast cell and dendritic cell lineages. Underlying this lineage diversion, L1 mediates binding of TCF-1 to its earliest target genes, which are subject to repression as T cells develop. These data suggest that the intrinsically disordered N terminus of TCF-1 maintains T cell lineage fidelity.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
A critical role for TCF-1 in T-lineage specification and differentiation.Nature. 2011 Aug 3;476(7358):63-8. doi: 10.1038/nature10279. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21814277 Free PMC article.
-
TCF-1 mediates repression of Notch pathway in T lineage-committed early thymocytes.Blood. 2013 May 9;121(19):4008-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-477349. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23660861 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lineage-Determining Transcription Factor TCF-1 Initiates the Epigenetic Identity of T Cells.Immunity. 2018 Feb 20;48(2):243-257.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.01.012. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 29466756 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin landscape and transcription factors in T cell programming.Trends Immunol. 2014 May;35(5):195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Trends Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24703587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of Lymphocyte Fate, Infection, and Tumor Immunity by TCF-1.Trends Immunol. 2019 Dec;40(12):1149-1162. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2019.10.006. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Trends Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31734149 Review.
Cited by
-
YY1 knockout in pro-B cells impairs lineage commitment, enabling unusual hematopoietic lineage plasticity.Genes Dev. 2024 Oct 16;38(17-20):887-914. doi: 10.1101/gad.351734.124. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 39362773 Free PMC article.
-
The epigenetic landscape of fate decisions in T cells.Nat Immunol. 2025 Apr;26(4):544-556. doi: 10.1038/s41590-025-02113-x. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Nat Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40108419 Review.
-
Transcriptional network dynamics in early T cell development.J Exp Med. 2024 Oct 7;221(10):e20230893. doi: 10.1084/jem.20230893. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39167073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomolecular condensates in immune cell fate.Nat Rev Immunol. 2025 Jun;25(6):445-459. doi: 10.1038/s41577-025-01130-z. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39875604 Review.
-
Wnt target gene activation requires β-catenin separation into biomolecular condensates.PLoS Biol. 2024 Sep 24;22(9):e3002368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002368. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39316611 Free PMC article.
References
Methods Only Reference
-
- Carleton M. et al. Signals transduced by CD3epsilon, but not by surface pre-TCR complexes, are able to induce maturation of an early thymic lymphoma in vitro. J Immunol 163, 2576–2585 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Ogilvy S. et al. Promoter elements of vav drive transgene expression in vivo throughout the hematopoietic compartment. Blood 94, 1855–1863 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA248041/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK112217/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA230800/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AI161873/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AI174776/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA052715/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK112217/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145754/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 AI112570/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK127768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI070077/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI091627/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI168240/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI168136/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

