Step-in dosing of bosutinib in pts with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) after second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy: results of the Bosutinib Dose Optimization (BODO) Study
- PMID: 37592092
- PMCID: PMC10492675
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-023-05394-0
Step-in dosing of bosutinib in pts with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) after second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy: results of the Bosutinib Dose Optimization (BODO) Study
Abstract
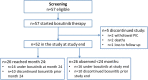
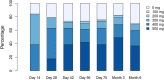
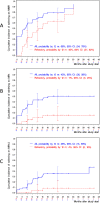
The approved dose of bosutinib in chronic phase CML is 400 mg QD in first-line and 500 mg QD in later-line treatment. However, given that gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity typically occurs early after treatment initiation, physicians often tend to start therapy with lower doses although this has never been tested systematically in prospective trials in the Western world. The Bosutinib Dose Optimization (BODO) Study, a multicenter phase II study, investigated the tolerability and efficacy of a step-in dosing concept of bosutinib (starting at 300 mg QD) in chronic phase CML patients in 2nd or 3rd line who were intolerant and/or refractory to previous TKI treatment. Of 57 patients included until premature closure of the study due to slow recruitment, 34 (60%) reached the targeted dose level of 500 mg QD following the 2-weekly step-in dosing regimen. While the dosing-in concept failed to reduce GI toxicity (grade II-IV, primary study endpoint) to < 40% (overall rate of 60%; 95% CI: 45-74%), bosutinib treatment (mean dosage: 403 mg/day) showed remarkable efficacy with a cumulative major molecular remission (MMR) rate of 79% (95% CI: 66 to 88%) at month 24. Of thirty patients refractory to previous therapy and not in MMR at baseline, 19 (64%) achieved an MMR during treatment. GI toxicity did not significantly impact on patient-reported outcomes (PRO) and led to treatment discontinuation in only one patient. Overall, the results of our trial support the efficacy and safety of bosutinib after failure of second-generation TKI pre-treatment. Trial registration: NCT02577926.
Keywords: Bosutinib; CML; Dose escalation; Efficacy; Gastrointestinal toxicity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SI reports advisory board honoraria from GSK, Pfizer, Incyte, and Novartis, honoraria from Novartis, BMS, Pfizer, Incyte, and AOP Orphan; and other financial support (e.g., travel support) from Alexion, Novartis, Pfizer, Mundipharma, Roche, Hexal, and AOP Orphan. LT reports advisory activity for Pfizer. MC reports honoraria from Pfizer, Incyte, Astra Zeneca, and Novartis. AB reports research funding from AOP health, honoraria from AOP Orphan, and membership on an entity´s board of directors or advisory committees from Gilead, Pfizer, and Incyte. AH reports research support from Novartis, Pfizer, BMS, and Incyte. SS reports research funding from Novartis, BMS, and Incyte and honoraria from Novartis, BMS, Incyte, Pfizer, and Roche. AK reports honoraria, advisory role, and travel support from Pfizer. JRG reports honoraria, advisory board membership, and consultancy roles for Pfizer. PS reports consulting/advisory role/honoraria/travel and accommodation support from Alexion, AOP Orphan, Blueprint Medicines, BMS/Celgene, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Sobi. FS reports honoraria from and consultancy for Abbvie, AOP Pharma, BMS/Celgene, Incyte, Novartis, and Pfizer. MH reports advisory board honoraria from Novartis and Pfizer and honoraria from Novartis. GF reports honoraria/advisory board honoraria from Novartis, Pfizer, and MSD and travel support from Gilead and Takeda. SK reports funding from Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb; advisory board honoraria from Pfizer, Incyte, Ariad, Novartis, and BMS; patent for BET inhibitor at RWTH Aachen University; honoraria from Novartis, BMS, Pfizer, Incyte, and Ariad; and other financial support (e.g., travel support) from Novartis, BMS, Incyte, Ariad, and Pfizer. DW reports advisory board honoraria, honoraria, and research support from Pfizer, BMS, Incyte, and Novartis. THB reports consultancy from Janssen, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer, research funding from Novartis and Pfizer, honoraria from Pfizer and Novartis, and other expenses (travel, accommodation, expenses) from Janssen, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer. KM, TI, AF, TE, HKA, AG, TP, MWU, UW, DK, and MP report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cortes JE, Kantarjian HM, Brummendorf TH, et al. Safety and efficacy of bosutinib (SKI-606) in chronic phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to imatinib. Blood. 2011;118(17):4567–4576. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-05-355594. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

