Effects of hydroalcoholic, methanolic, and hexane extracts of brown algae Sargassum angustifolium on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficit in rodents
- PMID: 37593166
- PMCID: PMC10427794
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.371585
Effects of hydroalcoholic, methanolic, and hexane extracts of brown algae Sargassum angustifolium on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficit in rodents
Abstract
Background and purpose: Properties of Alzheimer's disease, can be caused by several reasons and there is no definite treatment for it. We aimed to study the effect of the hydroalcoholic extract, methanolic and n-hexane fractions of brown algae Sargassum angustifolium on memory impairment in mice and rats.
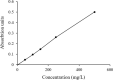
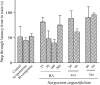
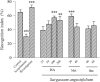
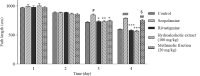
Experimental approach: Hydroalcoholic extract (25, 50, 100, 200 mg/kg), methanolic (20 and 40 mg/kg) and n-hexane (40 and 60 mg/kg) fractions of S. angustifolium were administered for 21 days intraperitoneally before scopolamine injection (2 mg/kg) on day 21. Rivastigmine was administered for 3 weeks intraperitoneally as well. Then, cognitive function was evaluated by three behavioral tests: passive avoidance, object recognition, and the Morris Water Maze test.
Findings/results: Scopolamine induced memory impairment and rivastigmine significantly reversed the memory dysfunction in all three tests. Hydroalcoholic extract and methanolic fraction significantly reversed scopolamine-induced memory impairment in passive avoidance by 64% and 55% and enhanced the recognition index in the object recognition test. In the Morris water maze test probe trial and training session, on days 3 and 4, the hydroalcoholic extract showed a significant decrease in time spent in the target quadrant and path length, respectively. Also, hydroalcoholic extract and methanolic fraction decreased escape latency time in training sessions on days 3 and 4, by 50% and 31% in comparison to scopolamine. N-hexane fractions had no significant effect on scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment.
Conclusion and implications: Although the n-hexane fraction wasn't effective, the administration of hydroalcoholic extract and the methanolic fraction of S. angustifolium enhanced scopolamine-induced memory impairment.
Keywords: Alzheimer; Morris water maze test; Object recognition; Passive avoidance; Sargassum angustifolium; Scopolamine.
Copyright: © 2023 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures




References
-
- Niu H, Alvarez-Alvarez I, Guillen-Grima F, Aguinaga-Ontoso I. Prevalence and incidence of Alzheimer's disease in europe: a meta-analysis. Neurologia. 2017;32(8):523–532. DOI: 10.1016/j.nrl.2016.02.016. - PubMed
-
- Amin MJ, Miana GA, Rashid U, Rahman KM, Khan HU, Sadiq A. SAR based in-vitro anticholinesterase and molecular docking studies of nitrogenous progesterone derivatives. Steroids. 2020;158:108599,1–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2020.108599. - PubMed
-
- Ozben T, Ozben S. Neuro-inflammation and anti-inflammatory treatment options for Alzheimer's disease. ClinBiochem. 2019;72:87–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2019.04.001. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
