Neurotoxicology of alcohol: a bibliometric and science mapping analysis
- PMID: 37593178
- PMCID: PMC10427875
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1209616
Neurotoxicology of alcohol: a bibliometric and science mapping analysis
Abstract
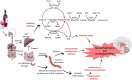
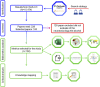
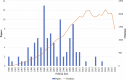
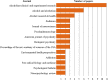
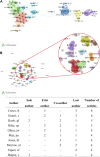
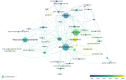
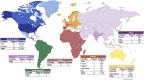
Alcohol consumption is common in many societies and has increased considerably, resulting in many socioeconomic and public health problems. In this sense, studies have been carried out in order to understand the mechanisms involved in alcohol consumption and related harmful effects. This study aimed to identify and map the knowledge and to perform bibliometric analysis of the neurotoxicology of alcohol based on the 100 most cited articles. A search was carried out in the Web of Science Core Collection database and information was extracted regarding the journal, authors, keywords, year of publication, number of citations, country and continent of the corresponding author. For each selected manuscript, the study design, alcohol exposure model, dose, period of exposure, and effect on the central nervous system and research hotspots were mapped. The journal with the highest number of publications was Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research (n = 11 papers), the author who contributed the most was Crews FT (n = 8 papers), the studies had a total of 288 keywords and 75% of the publications were from the United States of America. The experimental studies evaluated the effects of prenatal and postnatal exposure and were conducted in rats and mice using doses ranging from 2.5 to 14 g/kg/day, with administration by subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, intragastric, or inhalation route or with free access through drinking bottles. Among the studies mapped, the oldest one (1989) aimed to understand the systemic damage and mechanisms of action involved, while the most recent focused on understanding the receptors and mechanisms involved in addiction, as well as genetic factors. Our results show the panorama of the most widespread scientific production in the scientific community on the neurotoxicology of ethanol, a high prevalence was observed in studies that addressed fetal alcohol syndrome and/or the effects of ethanol on neurodevelopment.
Keywords: alcohol; alcohol abuse; alcoholism; bibliometric; central nervous system.
Copyright © 2023 Mendes, Baia-da-Silva, Melo, Bittencourt, Souza-Rodrigues, Fernandes, Maia and Lima.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

