Activating Inducible T-cell Costimulator Yields Antitumor Activity Alone and in Combination with Anti-PD-1 Checkpoint Blockade
- PMID: 37593752
- PMCID: PMC10430783
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0293
Activating Inducible T-cell Costimulator Yields Antitumor Activity Alone and in Combination with Anti-PD-1 Checkpoint Blockade
Abstract
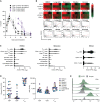
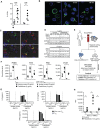
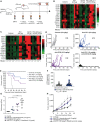
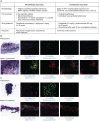
In recent years, there has been considerable interest in mAb-based induction of costimulatory receptor signaling as an approach to combat cancer. However, promising nonclinical data have yet to translate to a meaningful clinical benefit. Inducible T-cell costimulator (ICOS) is a costimulatory receptor important for immune responses. Using a novel clinical-stage anti-ICOS immunoglobulin G4 mAb (feladilimab), which induces but does not deplete ICOS+ T cells and their rodent analogs, we provide an end-to-end evaluation of the antitumor potential of antibody-mediated ICOS costimulation alone and in combination with programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade. We demonstrate, consistently, that ICOS is expressed in a range of cancers, and its induction can stimulate growth of antitumor reactive T cells. Furthermore, feladilimab, alone and with a PD-1 inhibitor, induced antitumor activity in mouse and humanized tumor models. In addition to nonclinical evaluation, we present three patient case studies from a first-time-in-human, phase I, open-label, dose-escalation and dose-expansion clinical trial (INDUCE-1; ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02723955), evaluating feladilimab alone and in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors. Preliminary data showing clinical benefit in patients with cancer treated with feladilimab alone or in combination with pembrolizumab was reported previously; with example cases described here. Additional work is needed to further validate the translation to the clinic, which includes identifying select patient populations that will benefit from this therapeutic approach, and randomized data with survival endpoints to illustrate its potential, similar to that shown with CTLA-4 and PD-1 blocking antibodies.
Significance: Stimulation of the T-cell activation marker ICOS with the anti-ICOS agonist mAb feladilimab, alone and in combination with PD-1 inhibition, induces antitumor activity across nonclinical models as well as select patients with advanced solid tumors.
© 2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

References
-
- Mayes PA, Hance KW, Hoos A. The promise and challenges of immune agonist antibody development in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2018;17:509–27. - PubMed
-
- Hoos A. Development of immuno-oncology drugs—from CTLA4 to PD1 to the next generations. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2016;15:235–47. - PubMed
-
- Hargadon KM, Johnson CE, Williams CJ. Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for cancer: an overview of FDA-approved immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int Immunopharmacol 2018;62:29–39. - PubMed
-
- Chen DS, Mellman I. Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013;39:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

