The Antimicrobial Properties of PdII - and RuII -pyta Complexes
- PMID: 37593808
- PMCID: PMC10947176
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202300247
The Antimicrobial Properties of PdII - and RuII -pyta Complexes
Abstract
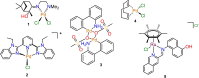
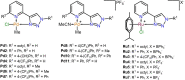
Infections associated with antimicrobial resistance (AMR) are poised to become the leading cause of death in the next few decades, a scenario that can be ascribed to two phenomena: antibiotic over-prescription and a lack of antibiotic drug development. The crowd-sourced initiative Community for Open Antimicrobial Drug Discovery (CO-ADD) has been testing research compounds contributed by researchers around the world to find new antimicrobials to combat AMR, and during this campaign has found that metallodrugs might be a promising, yet untapped source. To this end, we submitted 18 PdII - and RuII -pyridyl-1,2,3-triazolyl complexes that were developed as catalysts to assess their antimicrobial properties. It was found that the Pd complexes, especially Pd1, possessed potent antifungal activity with MICs between 0.06 and 0.125 μg mL-1 against Candida glabrata. The in-vitro studies were extended to in-vivo studies in Galleria mellonella larvae, where it was established that the compounds were nontoxic. Here, we effectively demonstrate the potential of PdII -pyta complexes as antifungal agents.
Keywords: AMR; antifungal drugs; inorganic medicinal chemistry; metalloantibiotics; metals in medicine.
© 2023 The Authors. ChemBioChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Murray C. J., Ikuta K. S., Sharara F., Swetschinski L., Robles Aguilar G., Gray A., Han C., Bisignano C., Rao P., Wool E., Johnson S. C., Browne A. J., Chipeta M. G., Fell F., Hackett S., Haines-Woodhouse G., Kashef Hamadani B. H., Kumaran E. A. P., McManigal B., Agarwal R., Akech S., Albertson S., Amuasi J., Andrews J., Aravkin A., Ashley E., Bailey F., Baker S., Basnyat B., Bekker A., Bender R., Bethou A., Bielicki J., Boonkasidecha S., Bukosia J., Carvalheiro C., Castañeda-Orjuela C., Chansamouth V., Chaurasia S., Chiurchiù S., Chowdhury F., Cook A. J., Cooper B., Cressey T. R., Criollo-Mora E., Cunningham M., Darboe S., Day N. P. J., De Luca M., Dokova K., Dramowski A., Dunachie S. J., Eckmanns T., Eibach D., Emami A., Feasey N., Fisher-Pearson N., Forrest K., Garrett D., Gastmeier P., Giref A. Z., Greer R. C., Gupta V., Haller S., Haselbeck A., Hay S. I., Holm M., Hopkins S., Iregbu K. C., Jacobs J., Jarovsky D., Javanmardi F., Khorana M., Kissoon N., Kobeissi E., Kostyanev T., Krapp F., Krumkamp R., Kumar A., Kyu H. H., Lim C., Limmathurotsakul D., Loftus M. J., Lunn M., Ma J., Mturi N., Munera-Huertas T., Musicha P., Mussi-Pinhata M. M., Nakamura T., Nanavati R., Nangia S., Newton P., Ngoun C., Novotney A., Nwakanma D., Obiero C. W., Olivas-Martinez A., Olliaro P., Ooko E., Ortiz-Brizuela E., Peleg A. Y., Perrone C., Plakkal N., Ponce-de-Leon A., Raad M., Ramdin T., Riddell A., Roberts T., Robotham J. V., Roca A., Rudd K. E., Russell N., Schnall J., Scott J. A. G., Shivamallappa M., Sifuentes-Osornio J., Steenkeste N., Stewardson A. J., Stoeva T., Tasak N., Thaiprakong A., Thwaites G., Turner C., Turner P., van Doorn H. R., Velaphi S., Vongpradith A., Vu H., Walsh T., Waner S., Wangrangsimakul T., Wozniak T., Zheng P., Sartorius B., Lopez A. D., Stergachis A., Moore C., Dolecek C., Naghavi M., Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. - PubMed

