OTTM: an automated classification tool for translational drug discovery from omics data
- PMID: 37594310
- PMCID: PMC10516341
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbad301
OTTM: an automated classification tool for translational drug discovery from omics data
Abstract
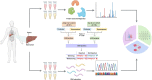
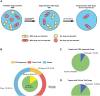
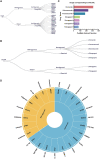
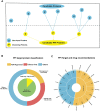
Omics data from clinical samples are the predominant source of target discovery and drug development. Typically, hundreds or thousands of differentially expressed genes or proteins can be identified from omics data. This scale of possibilities is overwhelming for target discovery and validation using biochemical or cellular experiments. Most of these proteins and genes have no corresponding drugs or even active compounds. Moreover, a proportion of them may have been previously reported as being relevant to the disease of interest. To facilitate translational drug discovery from omics data, we have developed a new classification tool named Omics and Text driven Translational Medicine (OTTM). This tool can markedly narrow the range of proteins or genes that merit further validation via drug availability assessment and literature mining. For the 4489 candidate proteins identified in our previous proteomics study, OTTM recommended 40 FDA-approved or clinical trial drugs. Of these, 15 are available commercially and were tested on hepatocellular carcinoma Hep-G2 cells. Two drugs-tafenoquine succinate (an FDA-approved antimalarial drug targeting CYC1) and branaplam (a Phase 3 clinical drug targeting SMN1 for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy)-showed potent inhibitory activity against Hep-G2 cell viability, suggesting that CYC1 and SMN1 may be potential therapeutic target proteins for hepatocellular carcinoma. In summary, OTTM is an efficient classification tool that can accelerate the discovery of effective drugs and targets using thousands of candidate proteins identified from omics data. The online and local versions of OTTM are available at http://otter-simm.com/ottm.html.
Keywords: OTTM; hepatocellular carcinoma; literature mining; omics data; translational drug discovery.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Target discovery from data mining approaches.Drug Discov Today. 2009 Feb;14(3-4):147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2008.12.005. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Drug Discov Today. 2009. PMID: 19135549 Review.
-
Data-Driven Discovery of Molecular Targets for Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Cancer Treatment.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jan 2;2021:2670573. doi: 10.1155/2021/2670573. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33490264 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of anticancer drugs for hepatocellular carcinoma through personalized genome-scale metabolic modeling.Mol Syst Biol. 2014 Mar 19;10(3):721. doi: 10.1002/msb.145122. Mol Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 24646661 Free PMC article.
-
An omics perspective on drug target discovery platforms.Brief Bioinform. 2020 Dec 1;21(6):1937-1953. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz122. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 31774113 Free PMC article.
-
High-dimensional biology to comprehend hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2008 Feb;5(1):45-60. doi: 10.1586/14789450.5.1.45. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2008. PMID: 18282123 Review.
Cited by
-
The 2024 Report on the Human Proteome from the HUPO Human Proteome Project.J Proteome Res. 2024 Dec 6;23(12):5296-5311. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00776. Epub 2024 Nov 8. J Proteome Res. 2024. PMID: 39514846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Montaner J, Ramiro L, Simats A, et al. Multilevel omics for the discovery of biomarkers and therapeutic targets for stroke. Nat Rev Neurol 2020;16(5):247–64. - PubMed
-
- Favier J, Amar L, Gimenez-Roqueplo A-P. Paraganglioma and phaeochromocytoma: from genetics to personalized medicine. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2015;11(2):101–11. - PubMed
-
- Wishart DS. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2016;15(7):473–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

