In vitro modeling of CD8+ T cell exhaustion enables CRISPR screening to reveal a role for BHLHE40
- PMID: 37595022
- PMCID: PMC11975459
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.ade3369
In vitro modeling of CD8+ T cell exhaustion enables CRISPR screening to reveal a role for BHLHE40
Abstract
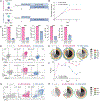
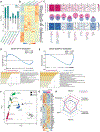
Identifying molecular mechanisms of exhausted CD8 T cells (Tex) is a key goal of improving immunotherapy of cancer and other diseases. However, high-throughput interrogation of in vivo Tex can be costly and inefficient. In vitro models of Tex are easily customizable and quickly generate high cellular yield, enabling CRISPR screening and other high-throughput assays. We established an in vitro model of chronic stimulation and benchmarked key phenotypic, functional, transcriptional, and epigenetic features against bona fide in vivo Tex. We leveraged this model of in vitro chronic stimulation in combination with CRISPR screening to identify transcriptional regulators of T cell exhaustion. This approach identified several transcription factors, including BHLHE40. In vitro and in vivo validation defined a role for BHLHE40 in regulating a key differentiation checkpoint between progenitor and intermediate Tex subsets. By developing and benchmarking an in vitro model of Tex, then applying high-throughput CRISPR screening, we demonstrate the utility of mechanistically annotated in vitro models of Tex.
Conflict of interest statement
E.J.W. is a member of the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy that supports research in the Wherry laboratory. E.J.W. is an advisor for Danger Bio, Marengo, Janssen, NewLimit, Pluto Immunotherapeutics Related Sciences, Santa Ana Bio, Synthekine, and Surface Oncology. E.J.W. is a founder of and holds stock in Surface Oncology, Danger Bio, and Arsenal Biosciences. O.K. holds equity in Arsenal Biosciences and is an employee of Orange Grove Bio. R.P.S. is an employee of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co. Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA.
Figures



Update of
-
In Vitro Modeling of CD8 T Cell Exhaustion Enables CRISPR Screening to Reveal a Role for BHLHE40.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 17:2023.04.17.537229. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.17.537229. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Sci Immunol. 2023 Aug 25;8(86):eade3369. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.ade3369. PMID: 37131713 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- McLane LM, Abdel-Hakeem MS, Wherry EJ, CD8 T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection and cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol 37, 457–495 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ, Ahmed R, Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 439, 682–687 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Leach DR, Krummel MF, Allison JP, Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science 271, 1734–1736 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- F30 AI129263/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI117950/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI115712/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K00 CA234842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI108545/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA210944/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI155577/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F99 CA234842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082630/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007442/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

