Sex-biased TGFβ signalling in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 37595264
- PMCID: PMC10597641
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvad129
Sex-biased TGFβ signalling in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
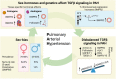
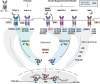
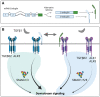
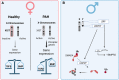
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare cardiovascular disorder leading to pulmonary hypertension and, often fatal, right heart failure. Sex differences in PAH are evident, which primarily presents with a female predominance and increased male severity. Disturbed signalling of the transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) family and gene mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2 (BMPR2) are risk factors for PAH development, but how sex-specific cues affect the TGFβ family signalling in PAH remains poorly understood. In this review, we aim to explore the sex bias in PAH by examining sex differences in the TGFβ signalling family through mechanistical and translational evidence. Sex hormones including oestrogens, progestogens, and androgens, can determine the expression of receptors (including BMPR2), ligands, and soluble antagonists within the TGFβ family in a tissue-specific manner. Furthermore, sex-related genetic processes, i.e. Y-chromosome expression and X-chromosome inactivation, can influence the TGFβ signalling family at multiple levels. Given the clinical and mechanistical similarities, we expect that the conclusions arising from this review may apply also to hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), a rare vascular disorder affecting the TGFβ signalling family pathway. In summary, we anticipate that investigating the TGFβ signalling family in a sex-specific manner will contribute to further understand the underlying processes leading to PAH and likely HHT.
Keywords: Activin; Androgen; BMP; BMPR2; Endothelial; HHT; Hypertension; Oestrogen; PAH; TGFβ.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, Badagliacca R, Berger RMF, Brida M, Carlsen J, Coats AJS, Escribano-Subias P, Ferrari P, Ferreira DS, Ghofrani HA, Giannakoulas G, Kiely DG, Mayer E, Meszaros G, Nagavci B, Olsson KM, Pepke-Zaba J, Quint JK, Rådegran G, Simonneau G, Sitbon O, Tonia T, Toshner M, Vachiery J-L, Noordegraaf AV, Delcroix M, Rosenkranz S; ESC/ERS Scientific Document Group . 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 2022;43:3618–3731.
-
- Yeager ME, Halley GR, Golpon HA, Voelkel NF, Tuder RM. Microsatellite instability of endothelial cell growth and apoptosis genes within plexiform lesions in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res 2001;88:E2–E11. - PubMed
-
- Ranchoux B, Antigny F, Rucker-Martin C, Hautefort A, Péchoux C, Bogaard HJ, Dorfmüller P, Remy S, Lecerf F, Planté S, Chat S, Fadel E, Houssaini A, Anegon I, Adnot S, Simonneau G, Humbert M, Cohen-Kaminsky S, Perros F. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2015;131:1006–1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

