Retropharyngeal Hematoma Causing Airway Compromise After Tissue Plasminogen Activator Administration: A Case Report
- PMID: 37595307
- PMCID: PMC10438936
- DOI: 10.5811/cpcem.1602
Retropharyngeal Hematoma Causing Airway Compromise After Tissue Plasminogen Activator Administration: A Case Report
Abstract
Introduction: Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), commonly used for treatment of acute ischemic stroke, is associated with life-threatening bleeding intracranially as well as surrounding the airway.
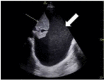
Case report: A 78-year-old year old male who presented with stroke symptoms and after tPA administration developed a retropharyngeal hematoma requiring intubation and surgical intervention.
Conclusion: Numerous threats to the patient's airway can develop after tPA administration. While angioedema is the most common cause, it is important to be prepared for other causes related to hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Demaerschalk BM, Kleindorfer DO, Adeoye OM, et al. American Heart Association Stroke Council and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Scientific Rationale for the Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2016;47(2):581–641. Erratum in: Stroke 2016;47(11):e262. - PubMed
-
- Hill MD, Lye T, Moss H, et al. Hemi-orolingual angioedema and ACE inhibition after alteplase treatment of stroke. Neurology. 2003;60(9):1525–7. - PubMed
-
- Gallant SC, Fritz MA, Paul BC, et al. Management of airway compromise following thyroid cyst hemorrhage after thrombolytic therapy. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(3):604–7. - PubMed
-
- Shaps HJ, Snyder GE, Sama AE, et al. Airway compromise secondary to lingual hematoma complicating administration of tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. Ann Emerg Med. 2001;38(4):447–9. - PubMed
