Segment anything model for medical image analysis: An experimental study
- PMID: 37595404
- PMCID: PMC10528428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2023.102918
Segment anything model for medical image analysis: An experimental study
Abstract
Training segmentation models for medical images continues to be challenging due to the limited availability of data annotations. Segment Anything Model (SAM) is a foundation model trained on over 1 billion annotations, predominantly for natural images, that is intended to segment user-defined objects of interest in an interactive manner. While the model performance on natural images is impressive, medical image domains pose their own set of challenges. Here, we perform an extensive evaluation of SAM's ability to segment medical images on a collection of 19 medical imaging datasets from various modalities and anatomies. In our experiments, we generated point and box prompts for SAM using a standard method that simulates interactive segmentation. We report the following findings: (1) SAM's performance based on single prompts highly varies depending on the dataset and the task, from IoU=0.1135 for spine MRI to IoU=0.8650 for hip X-ray. (2) Segmentation performance appears to be better for well-circumscribed objects with prompts with less ambiguity such as the segmentation of organs in computed tomography and poorer in various other scenarios such as the segmentation of brain tumors. (3) SAM performs notably better with box prompts than with point prompts. (4) SAM outperforms similar methods RITM, SimpleClick, and FocalClick in almost all single-point prompt settings. (5) When multiple-point prompts are provided iteratively, SAM's performance generally improves only slightly while other methods' performance improves to the level that surpasses SAM's point-based performance. We also provide several illustrations for SAM's performance on all tested datasets, iterative segmentation, and SAM's behavior given prompt ambiguity. We conclude that SAM shows impressive zero-shot segmentation performance for certain medical imaging datasets, but moderate to poor performance for others. SAM has the potential to make a significant impact in automated medical image segmentation in medical imaging, but appropriate care needs to be applied when using it. Code for evaluation SAM is made publicly available at https://github.com/mazurowski-lab/segment-anything-medical-evaluation.
Keywords: Deep learning; Foundation models; Segmentation.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
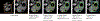
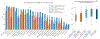

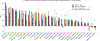
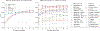



References
-
- Anna M, Hasnin, kaggle446, shirzad, Will C., yffud, 2016. Ultrasound nerve segmentation. URL: https://kaggle.com/competitions/ultrasound-nerve-segmentation.
-
- Anwar SM, Majid M, Qayyum A, Awais M, Alnowami M, Khan MK, 2018. Medical image analysis using convolutional neural networks: a review. Journal of medical systems 42, 1–13. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Geng Y, Chen Z, Horrocks I, Pan JZ, Chen H, 2021. Knowledge-aware zero-shot learning: Survey and perspective, in: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

