Molecular dynamics simulations support a multistep pathway for activation of branched actin filament nucleation by Arp2/3 complex
- PMID: 37595874
- PMCID: PMC10514467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105169
Molecular dynamics simulations support a multistep pathway for activation of branched actin filament nucleation by Arp2/3 complex
Abstract
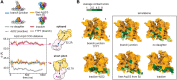
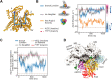
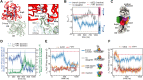
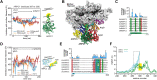
Actin-related protein 2/3 complex (Arp2/3 complex) catalyzes the nucleation of branched actin filaments that push against membranes in processes like cellular motility and endocytosis. During activation by WASP proteins, the complex must bind WASP and engage the side of a pre-existing (mother) filament before a branched filament is nucleated. Recent high-resolution structures of activated Arp2/3 complex revealed two major sets of activating conformational changes. How these activating conformational changes are triggered by interactions of Arp2/3 complex with actin filaments and WASP remains unclear. Here we use a recent high-resolution structure of Arp2/3 complex at a branch junction to design all-atom molecular dynamics simulations that elucidate the pathway between the active and inactive states. We ran a total of ∼4.6 microseconds of both unbiased and steered all-atom molecular dynamics simulations starting from three different binding states, including Arp2/3 complex within a branch junction, bound only to a mother filament, and alone in solution. These simulations indicate that the contacts with the mother filament are mostly insensitive to the massive rigid body motion that moves Arp2 and Arp3 into a short pitch helical (filament-like) arrangement, suggesting actin filaments alone do not stimulate the short pitch conformational change. In contrast, contacts with the mother filament stabilize subunit flattening in Arp3, an intrasubunit change that converts Arp3 from a conformation that mimics an actin monomer to one that mimics a filamentous actin subunit. Our results support a multistep activation pathway that has important implications for understanding how WASP-mediated activation allows Arp2/3 complex to assemble force-producing actin networks.
Keywords: Arp2/3 complex; WASP; actin; molecular dynamics; nucleation.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structure of Arp2/3 complex at a branched actin filament junction resolved by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 May 31;119(22):e2202723119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202723119. Epub 2022 May 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35622886 Free PMC article.
-
Role and structural mechanism of WASP-triggered conformational changes in branched actin filament nucleation by Arp2/3 complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 5;113(27):E3834-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1517798113. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27325766 Free PMC article.
-
Unconcerted conformational changes in Arp2/3 complex integrate multiple activating signals to assemble functional actin networks.Curr Biol. 2022 Mar 14;32(5):975-987.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 35090589 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling to actin assembly via the WASP (Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein)-family proteins and the Arp2/3 complex.Biochem J. 2004 May 15;380(Pt 1):1-17. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040176. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15040784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleation, stabilization, and disassembly of branched actin networks.Trends Cell Biol. 2022 May;32(5):421-432. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2021.10.006. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Trends Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34836783 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular simulation approaches to probing the effects of mechanical forces in the actin cytoskeleton.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2024 Aug;81(8):318-327. doi: 10.1002/cm.21837. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38334204 Free PMC article.
-
Changes Induced by P2X7 Receptor Stimulation of Human Glioblastoma Stem Cells in the Proteome of Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Their Secretome.Cells. 2024 Mar 25;13(7):571. doi: 10.3390/cells13070571. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607010 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying Unbiased Conformational Ensembles from Biased Simulations Using ShapeGMM.J Chem Theory Comput. 2024 May 14;20(9):3492-3502. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.4c00223. Epub 2024 Apr 25. J Chem Theory Comput. 2024. PMID: 38662196 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of Arp2/3 complex activation by nucleation-promoting factors and an actin monomer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Mar 11;122(10):e2421467122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2421467122. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40048273
References
-
- Siton-Mendelson O., Bernheim-Groswasser A. Functional actin networks under construction: the cooperative action of actin nucleation and elongation factors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017;42:414–430. - PubMed
-
- Amann K.J., Pollard T.D. The Arp2/3 complex nucleates actin filament branches from the sides of pre-existing filaments. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001;3:306–310. - PubMed
-
- Molinie N., Gautreau A. The Arp2/3 regulatory system and its deregulation in cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2018;98:215–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

