Renal pathology in adult and paediatric population of Japan: review of the Japan renal biopsy registry database from 2007 to 2017
- PMID: 37597092
- PMCID: PMC10638177
- DOI: 10.1007/s40620-023-01687-9
Renal pathology in adult and paediatric population of Japan: review of the Japan renal biopsy registry database from 2007 to 2017
Abstract
Background: The Japan Renal Biopsy Registry (J-RBR), a nationwide, web-based, registry system, started in 2007. This study aimed to summarise the epidemiology of biopsy-diagnosed kidney disease in Japan over 10 years.
Methods: We analysed the J-RBR database, from 2007 to 2017. Patients' clinical data collected at the time of biopsy and histopathological diagnoses were used for epidemiological and clinicopathologic analyses.
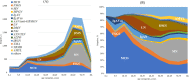
Results: The predominant renal biopsy diagnoses were immunoglobulin A nephropathy (39.2%), lupus nephritis (6.5%) and minimal change disease (6.0%) in younger adults (19-64 years), and membranous nephropathy (17.4%), antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis or anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis (13.0%), and immunoglobulin A nephropathy (12.5%) in older adults (≥ 65 years). The percentages of patients diagnosed with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis and immunoglobulin A nephropathy decreased, whereas those with immunoglobulin A vasculitis and diabetic nephropathy increased over the decade. In paediatric patients (< 19 years), immunoglobulin A nephropathy (36.1%), minimal change disease (17.6%), and immunoglobulin A vasculitis (8.6%) were the predominant diagnoses. The percentage of patients diagnosed with immunoglobulin A vasculitis increased over the decade. Based on the sex distribution, minimal change disease and membranous nephropathy were predominant in men aged < 20 and > 40 years, respectively, whereas immunoglobulin A vasculitis and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis or anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis were predominant in women in their 20s and 30s and aged < 50 years, respectively. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy was predominant in men at most ages and in women in their 20s to 40s.
Conclusions: This study describes the distribution and changes in kidney biopsy diagnoses over 10 years in Japan and paves the way for future research on kidney diseases in adults and children.
Keywords: Disease aetiology; Japan renal biopsy registry; Kidney biopsy; Renal pathology.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hamano T, Imaizumi T, Hasegawa T, Fujii N, Komaba H, Ando M, Nangaku M, Nitta K, Hirakata H, Isaka Y, Wada T, Maruyama S, Fukagawa M. Biopsy-proven CKD etiology and outcomes: chronic kidney disease Japan Cohort (CKD-JAC) study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfac134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama H, Yokoyama H, Sato H, Saito T, Kohda Y, Nishi S, Tsuruya K, Kiyomoto H, Iida H, Sasaki T, Higuchi M, Hattori M, Oka K, Kagami S, Nagata M, Kawamura T, Honda M, Fukasawa Y, Fukatsu A, Morozumi K, Yoshikawa N, Yuzawa Y, Matsuo S, Kiyohara Y, Joh K, Taguchi T, Makino H, Committee for Standardization of Renal Pathological Diagnosis and Working Group for Renal Biopsy Database, Japanese Society of Nephrology, Tokyo, Japan Japan renal biopsy registry: the first nationwide, web-based, and prospective registry system of renal biopsies in Japan. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011;15:493–503. doi: 10.1007/s10157-011-0430-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama H, Sugiyama H, Sato H, Taguchi T, Nagata M, Matsuo S, Makino H, Watanabe T, Saito T, Kiyohara Y, Nishi S, Iida H, Morozumi K, Fukatsu A, Sasaki T, Tsuruya K, Kohda Y, Higuchi M, Kiyomoto H, Goto S, Hattori M, Hataya H, Kagami S, Yoshikawa N, Fukasawa Y, Ueda Y, Kitamura H, Shimizu A, Oka K, Nakagawa N, Ito T, Uchida S, Furuichi K, Nakaya I, Umemura S, Hiromura K, Yoshimura M, Hirawa N, Shigematsu T, Fukagawa M, Hiramatsu M, Terada Y, Uemura O, Kawata T, Matsunaga A, Kuroki A, Mori Y, Mitsuiki K, Yoshida H, Committee for the Standardization of Renal Pathological Diagnosis and for Renal Biopsy and Disease Registry of the Japanese Society of Nephrology, and the Progressive Renal Disease Research of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan Renal disease in the elderly and the very elderly Japanese: analysis of the Japan renal biopsy registry (J-RBR) Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012;16:903–920. doi: 10.1007/s10157-012-0673-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama H, Yokoyama H, Sato H, Saito T, Kohda Y, Nishi S, Tsuruya K, Kiyomoto H, Iida H, Sasaki T, Higuchi M, Hattori M, Oka K, Kagami S, Kawamura T, Takeda T, Hataya H, Fukasawa Y, Fukatsu A, Morozumi K, Yoshikawa N, Shimizu A, Kitamura H, Yuzawa Y, Matsuo S, Kiyohara Y, Joh K, Nagata M, Taguchi T, Makino H, Committee for Standardization of Renal Pathological Diagnosis, Committee for Kidney Disease Registry, Japanese Society of Nephrology Japan renal biopsy registry and Japan kidney disease registry: committee report for 2009 and 2010. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2013;17:155–173. doi: 10.1007/s10157-012-0746-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

