Association of PIK3CA mutation with outcomes in HER2-positive breast cancer treated with anti-HER2 therapy: A meta-analysis and bioinformatic analysis of TCGA‑BRCA data
- PMID: 37597296
- PMCID: PMC10458974
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101738
Association of PIK3CA mutation with outcomes in HER2-positive breast cancer treated with anti-HER2 therapy: A meta-analysis and bioinformatic analysis of TCGA‑BRCA data
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to comprehensively explore the clinical significance of PIK3CA mutation in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer treated with anti-HER2 therapy.
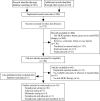
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane databases for eligible studies assessing the association between PIK3CA mutation and outcomes in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer receiving anti-HER2 therapy. The main outcomes included: (1) pathological complete response (pCR) or disease-free survival (DFS) for the neoadjuvant setting; (2) DFS or invasive DFS for the adjuvant setting; (3) objective response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), time-to-progression (TTP), or overall survival (OS) for the metastatic setting. The mutational landscape of HER2-positive breast cancer according to PIK3CA mutation status was examined based on TCGA breast cancer dataset.
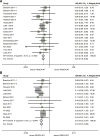
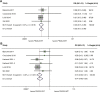
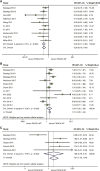
Results: Totally, 43 eligible studies, covering 11,099 patients with available data on PIK3CA mutation status, were identified. In the neoadjuvant setting, PIK3CA mutation was significantly associated with a lower pCR rate (OR=0.23, 95% CI 0.19-0.27, p<0.001). This association remained significant irrespective of the type of anti-HER2 therapy (single-agent or dual-agent) and hormone receptor status. There were no significant differences in DFS between PIK3CA mutated and wild-type patients in either the neoadjuvant or adjuvant settings. In the metastatic setting, PIK3CA mutation predicted worse ORR (OR=0.26, 95%CI 0.17-0.40, p<0.001), PFS (HR=1.28, 95%CI 1.03-1.59, p = 0.024) and TTP (HR=2.27, 95%CI 1.54-3.34, p<0.001). However, no significant association was observed between PIK3CA mutation status and OS. Distinct mutational landscapes were observed in HER2-positive breast cancer between individuals with PIK3CA mutations and those with wild-type PIK3CA.
Conclusions: PIK3CA mutation was significantly associated with a lower pCR rate in HER2-positive breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant anti-HER2 therapy. In the metastatic setting, PIK3CA mutation was predictive of worse ORR, PFS and TTP. These results suggest the potential for developing PI3K inhibitors as a therapeutic option for these patients.
Keywords: Anti-HER2 therapy; Breast cancer; HER2-positive; PIK3CA mutation; Predictive.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest All authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Slamon D.J., Clark G.M., Wong S.G., Levin W.J., Ullrich A., McGuire W.L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/NEU oncogene. Science. 1987;235(4785):177–182. - PubMed
-
- Loibl S., Gianni L. HER2-positive breast cancer. Lancet. 2017;389(10087):2415–2429. - PubMed
-
- Zardavas D., Te Marvelde L., Milne R.L., Fumagalli D., Fountzilas G., Kotoula V., Razis E., Papaxoinis G., Joensuu H., Moynahan M.E., et al. Tumor PIK3CA genotype and prognosis in early-stage breast cancer: a pooled analysis of individual patient data. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36(10):981–990. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

