Predicting Incident Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus or Gastric Cardia Using Machine Learning of Electronic Health Records
- PMID: 37597631
- PMCID: PMC11013733
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.08.011
Predicting Incident Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus or Gastric Cardia Using Machine Learning of Electronic Health Records
Abstract
Background & aims: Tools that can automatically predict incident esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma (GCA) using electronic health records to guide screening decisions are needed.
Methods: The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse was accessed to identify Veterans with 1 or more encounters between 2005 and 2018. Patients diagnosed with EAC (n = 8430) or GCA (n = 2965) were identified in the VHA Central Cancer Registry and compared with 10,256,887 controls. Predictors included demographic characteristics, prescriptions, laboratory results, and diagnoses between 1 and 5 years before the index date. The Kettles Esophageal and Cardia Adenocarcinoma predictioN (K-ECAN) tool was developed and internally validated using simple random sampling imputation and extreme gradient boosting, a machine learning method. Training was performed in 50% of the data, preliminary validation in 25% of the data, and final testing in 25% of the data.
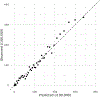
Results: K-ECAN was well-calibrated and had better discrimination (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [AuROC], 0.77) than previously validated models, such as the Nord-Trøndelag Health Study (AuROC, 0.68) and Kunzmann model (AuROC, 0.64), or published guidelines. Using only data from between 3 and 5 years before index diminished its accuracy slightly (AuROC, 0.75). Undersampling men to simulate a non-VHA population, AUCs of the Nord-Trøndelag Health Study and Kunzmann model improved, but K-ECAN was still the most accurate (AuROC, 0.85). Although gastroesophageal reflux disease was strongly associated with EAC, it contributed only a small proportion of gain in information for prediction.
Conclusions: K-ECAN is a novel, internally validated tool predicting incident EAC and GCA using electronic health records data. Further work is needed to validate K-ECAN outside VHA and to assess how best to implement it within electronic health records.
Keywords: Electronic Health Records; Esophageal Neoplasms; Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease; Mass Screening; Stomach Neoplasms.
Copyright © 2023 AGA Institute. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts of Interest:
JHR has received research support from Lucid Diagnostics. LPW is a consultant for Gilead Sciences. None of the other authors have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


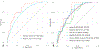


References
-
- Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, et al. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on the management of Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology 2011;140:1084–91. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald RC, di Pietro M, Ragunath K, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Barrett's oesophagus. Gut 2014;63:7–42. - PubMed
-
- Qumseya B, Sultan S, Bain P, et al. ASGE guideline on screening and surveillance of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 2019;90:335–359.e2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

