Predicting HPV association using deep learning and regular H&E stains allows granular stratification of oropharyngeal cancer patients
- PMID: 37598255
- PMCID: PMC10439941
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-023-00901-z
Predicting HPV association using deep learning and regular H&E stains allows granular stratification of oropharyngeal cancer patients
Abstract
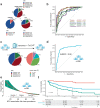
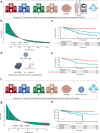
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer (OPSCC) represents an OPSCC subgroup with an overall good prognosis with a rising incidence in Western countries. Multiple lines of evidence suggest that HPV-associated tumors are not a homogeneous tumor entity, underlining the need for accurate prognostic biomarkers. In this retrospective, multi-institutional study involving 906 patients from four centers and one database, we developed a deep learning algorithm (OPSCCnet), to analyze standard H&E stains for the calculation of a patient-level score associated with prognosis, comparing it to combined HPV-DNA and p16-status. When comparing OPSCCnet to HPV-status, the algorithm showed a good overall performance with a mean area under the receiver operator curve (AUROC) = 0.83 (95% CI = 0.77-0.9) for the test cohort (n = 639), which could be increased to AUROC = 0.88 by filtering cases using a fixed threshold on the variance of the probability of the HPV-positive class - a potential surrogate marker of HPV-heterogeneity. OPSCCnet could be used as a screening tool, outperforming gold standard HPV testing (OPSCCnet: five-year survival rate: 96% [95% CI = 90-100%]; HPV testing: five-year survival rate: 80% [95% CI = 71-90%]). This could be confirmed using a multivariate analysis of a three-tier threshold (OPSCCnet: high HR = 0.15 [95% CI = 0.05-0.44], intermediate HR = 0.58 [95% CI = 0.34-0.98] p = 0.043, Cox proportional hazards model, n = 211; HPV testing: HR = 0.29 [95% CI = 0.15-0.54] p < 0.001, Cox proportional hazards model, n = 211). Collectively, our findings indicate that by analyzing standard gigapixel hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) histological whole-slide images, OPSCCnet demonstrated superior performance over p16/HPV-DNA testing in various clinical scenarios, particularly in accurately stratifying these patients.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
J.H. received consulting and lecture fees from BMS, also received research funding from CureVac. R.B. received consulting and lecture fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Illumina, Lilly, Merck-Serono, MSD, Novartis, Qiagen, Pfizer, Roche, Targos MP Inc. R.B. is Co-Founder and Scientific Advisor for Targos Mol. Pathology Inc and member of the Directory Board Gnothis Inc. H.C.R. received consulting and lecture fees from Novartis, Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Vertex and Merck. H.C.R. received research funding from AstraZeneca and Gilead Pharmaceuticals. HCR is a co-founder of CDL Therapeutics GmbH. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

