Systemic insecticides for control of stem gall wasp in highbush blueberry
- PMID: 37598313
- PMCID: PMC10564264
- DOI: 10.1093/jee/toad162
Systemic insecticides for control of stem gall wasp in highbush blueberry
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Systemic insecticides for control of stem gall wasp in highbush blueberry.J Econ Entomol. 2024 Apr 12;117(2):672. doi: 10.1093/jee/toae008. J Econ Entomol. 2024. PMID: 38241615 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
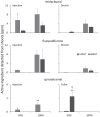
The gall wasp, Hemadas nubilipennis Ashmead, is a pest of highbush and lowbush blueberry and can pose a challenge to control with foliar sprays due to adult activity being during bloom and because larval development is within plant tissues. We hypothesized that systemic insecticides that move within the blueberry vascular system would reach areas where H. nubilipennis eggs are laid, causing larval mortality. Three application methods, crown injection, soil drench, and foliar spray were applied to potted 'Jersey' blueberry bushes at 50% and 100% rates to quantify systemic residue concentrations in shoots and leaves. Additionally, systemic insecticides were evaluated for control of gall wasps using single-shoot bioassays and measuring larval mortality at 0.01%, 0.1%, 1%, and 10% of field rate provided within a floral pick. Systemic insecticides tested in both studies included imidacloprid, flupyradifurone, and spirotetramat. The potted bush residue study determined that insecticides moved from three tested sites of entry: the roots, crown cavity, and foliage. Results from the shoot bioassays found that the mean percent larval survival of H. nubilipennis was negatively correlated with the concentration of AI detected in galls. Imidacloprid and spirotetramat were found to have the greatest potential for control of H. nubilipennis due to mortality in the shoot bioassays and similar residue concentrations in the potted bush studies to shoot bioassays. Future research should evaluate systemic insecticides applied in highbush blueberry plantings for control of H. nubilipennis using the bioassay mortality assessment method developed in this study.
Keywords: blueberry; gall wasp; injection; soil drench; systemic insecticide.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Entomological Society of America.
Figures





References
-
- Campana RJ. Characteristics of successful systemic chemicals. In: Proceedings of Symposium on Systemic Chemical Treatments in Tree Culture, October 9–11, 1978, Held at Michigan State University, Kellogg Center for Continuing Education, East Lansing, MI; 1978.
-
- Chaney WR. Physiology of introduced chemical movement. In: Proceedings of Symposium on Systemic Chemical Treatments in Tree Culture, October 9–11, 1978, Held at Michigan State University, Kellogg Center for Continuing Education, East Lansing, MI; 1978.
-
- Coslor CC, Vandervoort C, Wise JC.. Control of insect pests using trunk injection in a newly established apple orchard. Int J Fruit Sci. 2019b:19(2):151–164. 10.1080/15538362.2018.1501634. - DOI
-
- Doccola J, Wild P.. Insecticides: basic and other applications. In: Soloneski S, Larramendy M, editors.. Tree injection as an alternative method of insecticide application, insecticides—basic and other applications. Rijeka (Croatia): InTech; 2012. p. 61–78.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

