Is intraoperative embolization with n-butyl cyanoacrylate an alternative option in carotid body tumors surgery? A case report
- PMID: 37598489
- PMCID: PMC10462829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108636
Is intraoperative embolization with n-butyl cyanoacrylate an alternative option in carotid body tumors surgery? A case report
Abstract
Introduction and importance: The risk of intraoperative bleeding is relatively considerable because carotid body tumors (CBT) have rich vascular structures. Aim is to reduce intraoperative bleeding with preoperative embolization. We present a unique technique for the successful surgical removal of a challenging CBT using intraoperative direct percutaneous intratumoral n-butyl cyanoacrylate (n-BCA) embolization in a patient whose preoperative embolization failed and the operation could not be continued due to intraoperative bleeding.
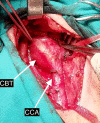
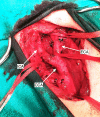
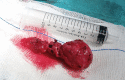
Clinical presentation: A 67-year-old female patient presented with 7 cm Shamblin class 3 CBT on her right neck. Due to the failure of the preoperative embolization, bleeding developed during the operation. In the case of Shamblin class 3 CBT, the primary concern was not the volume of bleeding, but the difficulty in seeing the dissection line due to hemorrhage. Intraoperative n-BCA straight embolization totally controlled the bleeding. The CBT was then readily removed.
Clinical discussion: Effective management of intraoperative hemorrhage is essential to ensure successful progression of surgical procedures of CBT. Hemorrhage causes complete disappearance of the dissection line, which is already difficult to detect due to adventitia invasion. It is clear that another method is needed when preoperative embolization or covered stenting fails. n-BCA has been used in the endovenous treatment of varicose veins for a long time, but to the best of our knowledge, there is no other case of its use in intraoperative CBT embolization.
Conclusion: Direct intraoperative embolization with n-BCA may be an alternative when other techniques are insufficient.
Keywords: Carotid body tumor; Glomus tumor; Intraoperative embolization; n-butyl cyanoacrylate.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement None.
Figures
References
-
- Agha R.A., Franchi T., Sohrab C., Mathew G., Kirwan A., Thomas A., et al. The SCARE 2020 guideline: updating consensus surgical case report (SCARE) guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2020;84(1):226–230. - PubMed
-
- Texakalidis P., Charisis N., Giannopoulos S., Xenos D., Rangel-Castilla L., Tassiopoulos A.K., Jabbour P., Grossberg J.A., Machinis T. Role of preoperative embolization in carotid body tumor surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019 Sep;129:503–513.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.05.209. (Epub 2019 May 30. PMID: 31154101) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jackson R.S., Myhill J.A., Padhya T.A., McCaffrey J.C., McCaffrey T.V., Mhaskar R.S. The effects of preoperative embolization on carotid body paraganglioma surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015 Dec;153(6):943–950. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources