Disrupted endoplasmic reticulum-mediated autophagosomal biogenesis in a Drosophila model of C9-ALS-FTD
- PMID: 37599467
- PMCID: PMC10761023
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2249750
Disrupted endoplasmic reticulum-mediated autophagosomal biogenesis in a Drosophila model of C9-ALS-FTD
Abstract
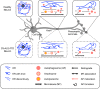
3R: UAS construct expressing 3 G4C2 repeats (used as control); 3WJ: three-way junction; 12R: UAS construct expressing leader sequence and 12 G4C2 repeats; 30R: UAS construct expressing 30 G4C2 repeats; 36R: UAS construct expressing 36 G4C2 repeats; 44R: UAS construct expressing leader sequence and 44 G4C2 repeats; ALS: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Atg: autophagy related; atl: atlastin; C9-ALS-FTD: ALS or FTD caused by hexanuleotide repeat expansion in C9orf72; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; FTD: frontotemporal dementia; HRE: GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat expansion; HSP: hereditary spastic paraplegia; Lamp1: lysosomal associated membrane protein 1; MT: microtubule; NMJ: neuromuscular junction; Rab: Ras-associated binding GTPase; RAN: repeat associated non-AUG (RAN) translation; RO-36: UAS construct expression "RNA-only" version of 36 G4C2 repeats in which stop codons in all six reading frames are inserted.; Rtnl1: Reticulon-like 1; SN: segmental nerve; TFEB/Mitf: transcription factor EB/microphthalmia associated transcription factor (Drosophila ortholog of TFEB); TrpA1: transient receptor potential cation channel A1; VAPB: VAMP associated protein B and C; VNC: ventral nerve cord (spinal cord in Drosophila larvae).
Keywords: Autophagy; C9-ALS-FTD; Drosophila; axonal transport; endoplasmic reticulum (ER) dynamics; motor neuron.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, et al. Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature. 2006. Jun 15;441(7095):880–884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
