Factors associated with parental intention to vaccinate their preschool children against COVID-19: a cross-sectional survey in urban area of Jakarta, Indonesia
- PMID: 37599811
- PMCID: PMC10435772
- DOI: 10.7774/cevr.2023.12.3.240
Factors associated with parental intention to vaccinate their preschool children against COVID-19: a cross-sectional survey in urban area of Jakarta, Indonesia
Abstract
Purpose: We reported a survey-based study assessing the parental intention to vaccinate children of 5 to 7 years old against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The aim of this study is to assess factors influencing the parental intention to vaccinate their children against COVID-19.
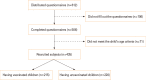
Materials and methods: This study adopted a cross-sectional design, held at the public health center of Senen district, Jakarta, Indonesia from November 1-30, 2022. The off-line questionnaires were distributed via the school administrator to all eligible parents. Factors associated with intention to vaccinate were analyzed with the regression logistic models.
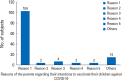
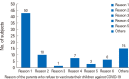
Results: Of the 435 parents in this study, 215 had already vaccinated their children against COVID-19 (49.4%), and the overall intention of the participants to vaccinate was 69.7%. Factors associated with intention to vaccinate the children against COVID-19 were parental employment status, parental COVID-19 vaccine status and concern of contracting COVID-19. Parents who are employed, had completed vaccines with COVID-19 booster vaccine, and had concern of their children contracting COVID-19 were more likely to vaccinate their children (odds ratio [OR], 2.10; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.22-3.69; p=0.011; OR, 2.15; 95% CI, 1.21-3.83; p=0.013; OR, 2.40; 95% CI, 1.34-4.30; p=0.004, respectively). Concern on the vaccine's side effects was negatively associated with the willingness to vaccinate.
Conclusion: This study showed that childhood COVID-19 vaccine only covered half of the population, with parental intentions for childhood COVID-19 vaccination being high, reaching almost two-thirds of the study participants. Factors influencing parental intentions were employment status, parental COVID-19 vaccine status, concerns about COVID-19 and concerns about vaccine side effects.
Keywords: COVID-19; Indonesia; Intention; Parents; Pediatrics; Vaccination.
© Korean Vaccine Society.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020;323:1239–1242. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023. [cited 2023 Feb 8]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Indonesian Task Force for COVID-19. COVID-19: confirmed local and area distribution map [Internet] [place unknown]: Indonesian task force for COVID-19; 2023. [cited 2023 Feb 8]. Available from: https://covid19.go.id/peta-sebaran.
-
- Pulungan AB. Indonesia set to have world’s highest rate of child deaths from COVID-19 [Internet] Jakarta: APPA Bulletin; 2020. [cited 2021 Sep 18]. Available from: http://a-p-p-a.org/pdf/1202-APPA-Bulletin-79-69-may-aug-2020.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

