Effect of Spice Incorporation on Sensory and Physico-chemical Properties of Matcha-Based Hard Candy
- PMID: 37599978
- PMCID: PMC10433358
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02574
Effect of Spice Incorporation on Sensory and Physico-chemical Properties of Matcha-Based Hard Candy
Abstract
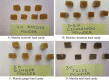
The present study was carried out to formulate and determine the sensory, proximate, phytochemical, and antioxidant properties of matcha hard candies incorporated with spices such as ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.), cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum and Cinnamon cassia), and holy basil (tulsi) (Ocimum sanctum L.). Standardized matcha (Camellia sinensis) hard candy was taken as a control, and spices/herbs were incorporated in different concentrations. The best formulation was GC5 (2% ginger powder) for matcha ginger hard candy, CZ10 (0.9% cinnamon powder) for matcha cinnamon hard candy, and TC7 (3% tulsi powder) for matcha tulsi hard candy. These formulations were selected based on the organoleptic evaluation. Furthermore, these selected hard candies were evaluated for the determination of proximate, phytochemical, and antioxidant profiles which exhibited significant results. This study demonstrates the excellent nutritional and phytochemical potential that spiced matcha hard candy has for use as a nutraceutical food product.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
-
- Embuscado M. E. Spices and herbs Natural sources of antioxidants a mini-review. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 811–819. 10.1016/j.jff.2015.03.005. - DOI
-
- Vijayan K. K.; AjithanThampuran R. V.. Pharmacology and Toxicology of Cinnamon and Cassia. In Cinnamon and Cassia; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2004; pp 259–284.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources