Effect of Modified Peristaltic Phacoemulsification Device on Efficiency and Post-Occlusion Pressure Surge
- PMID: 37600145
- PMCID: PMC10438468
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S416604
Effect of Modified Peristaltic Phacoemulsification Device on Efficiency and Post-Occlusion Pressure Surge
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate efficiency of grooving, nuclear fragment removal, and changes in pressure control in the Oertli Faros using traditional peristaltic and Speed and Precision (SPEEP) features. The SPEEP mode uses novel peristaltic technology permitting independent control of flow and vacuum.
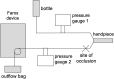
Methods: A porcine lens model was used with an enclosed chamber simulating the anterior segment. Grooving efficiency is evaluated with flow rates of 10, 30, and 50 mL/min using whole lenses. Lens cubes were emulsified at 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100% power with both SPEEP and non-SPEEP modes. Surge was evaluated with pressure gauges placed on the irrigation tubing and aspiration tubing. Pressure readings were recorded per the following: fluid and vacuum were initiated for 15 seconds, vacuum tubing was occluded for 5 seconds, tubing patency was then re-introduced for 15 seconds. Differences between sensors were recorded.
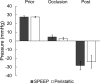
Results: No significant increase in efficiency was seen with increasing flow rate from 30 to 50 mL/min using SPEEP. No significant differences were shown in lens fragment removal in SPEEP and non-SPEEP modes at any power tested. Pressure difference measurements were not significantly different with SPEEP and non-SPEEP modes.
Conclusion: We showed that lower flow rates show comparable efficiency of grooving when using the SPEEP mode. The SPEEP function did not show increased efficiency in nuclear fragment removal when compared to traditional mode. Surge control was also comparable with both SPEEP and non-SPEEP modes. We suggest that the SPEEP function included in the Oertli Faros may have some advantages.
Keywords: cataract; grooving; machine setting optimization; nuclear fragment removal; power; pump.
© 2023 Ricks et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Olson is on the Board of Directors and equity owner of Perceive Bio and TMClear; Scientific Advisory Board and equity owner of Perfect Lens. Dr. Jeff Pettey reports a consulting agreement for Lensar and Zeiss, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Oertli® SPEEP – SPEED and precision. Berneck, Switzerland: Oertli Instrumente; 2021. Available from: https://www.oertli-instruments.com/en-us/surgical-platforms/catarhex-3/m.... Accessed March 13, 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

