Research progress of mitophagy in chronic cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 37600521
- PMCID: PMC10434995
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1224633
Research progress of mitophagy in chronic cerebral ischemia
Abstract
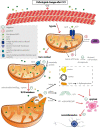
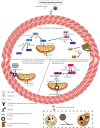
Chronic cerebral ischemia (CCI), a condition that can result in headaches, dizziness, cognitive decline, and stroke, is caused by a sustained decrease in cerebral blood flow. Statistics show that 70% of patients with CCI are aged > 80 years and approximately 30% are 45-50 years. The incidence of CCI tends to be lower, and treatment for CCI is urgent. Studies have confirmed that CCI can activate the corresponding mechanisms that lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, which, in turn, can induce mitophagy to maintain mitochondrial homeostasis. Simultaneously, mitochondrial dysfunction can aggravate the insufficient energy supply to cells and various diseases caused by CCI. Regulation of mitophagy has become a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of CCI. This article reviews the latest progress in the important role of mitophagy in CCI and discusses the induction pathways of mitophagy in CCI, including ATP synthesis disorder, oxidative stress injury, induction of reactive oxygen species, and Ca2+ homeostasis disorder, as well as the role of drugs in CCI by regulating mitophagy.
Keywords: chronic cerebral ischemia; mitochondrial autophagy; oxidative stress; stroke; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Yu, Zhang, Fu, Wu, Yin and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The critical roles of mitophagy in cerebral ischemia.Protein Cell. 2016 Oct;7(10):699-713. doi: 10.1007/s13238-016-0307-0. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Protein Cell. 2016. PMID: 27554669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in the regulatory mechanism of mitophagy in chronic cerebral ischemic neuronal injury.Exp Neurol. 2025 Jan;383:115003. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.115003. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Exp Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39419436 Review.
-
The neuroprotective effect of Chinese herbal medicine for cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through regulating mitophagy.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 4;15:1378358. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1378358. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38895624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dengzhan Xixin injection derived from a traditional Chinese herb Erigeron breviscapus ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via modulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial apoptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Apr 24;288:114988. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.114988. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35032588
-
Mitophagy in Cerebral Ischemia and Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jun 8;13:687246. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.687246. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34168551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic effects and mechanisms of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in neurocognitive disorders.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2025 Apr 17;18:17562864251332035. doi: 10.1177/17562864251332035. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2025. PMID: 40291753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Improves Chronic Ischemic Hippocampal Damage Associated with Suppression of IRE1α/TRAF2/ASK1/JNK-Dependent Apoptosis.Inflammation. 2024 Aug;47(4):1479-1490. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-01989-5. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38401021 Free PMC article.
-
Potential application of traditional Chinese medicine in age-related macular degeneration-focusing on mitophagy.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 17;15:1410998. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1410998. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38828456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous