Hypereosinophilic Syndrome with Pulmonary Involvement in Ulcerative Colitis
- PMID: 37600609
- PMCID: PMC10435027
- DOI: 10.1097/PG9.0000000000000320
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome with Pulmonary Involvement in Ulcerative Colitis
Abstract
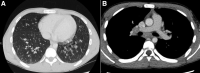
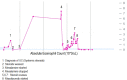
Reactive eosinophilia is associated with inflammatory bowel disease and is more common in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) compared with Crohn's disease. The prevalence rate of peripheral blood eosinophilia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease has been described to be as high as 30%-40% of patients in a pediatric study. The coexistence of hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and UC is uncommon. We present a 15-year-old boy with UC associated with HES who presented with chest pain and shortness of breath. Laboratory evaluation showed marked eosinophilia. Alternative causes of eosinophilia including eosinophilic leukemia, infections, or drug-induced eosinophilic pneumonia were ruled out. The patient was ultimately diagnosed with HES responsive to mepolizumab.
Keywords: eosinophilia; hypereosinophilic syndrome; ulcerative colitis.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sadi G, Yang Q, Dufault B, et al. Prevalence of peripheral eosinophilia at diagnosis in children with inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016;62:573–576. - PubMed
-
- Awano N, Ryu T, Yoshimura N, et al. Successful treatment of ulcerative colitis associated with hypereosinophilic syndrome/chronic eosinophilic leukemia. Intern Med. 2011;50:1741–1745. - PubMed
-
- Marina S, Pedro L, Angel F, et al. Case report: hypereosinophilic syndrome response to infliximab in a patient with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterol Hepatol Open Access. 2016;5:00158.
-
- Terrier B, Fontaine H, Schmitz J, et al. Coexistence and parallel evolution of hypereosinophilic syndrome, autoimmune hepatitis, and ulcerative colitis suggest common pathogenic features. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1132–1134. - PubMed
-
- Patel B, Butterfield JH, Weiler CR, et al. Tolerance and efficacy with simultaneous use of two monoclonal antibodies for a patient with hypereosinophilic syndrome and ulcerative colitis. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2016;35:300–303. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

