Activated PI3Kδ syndrome - reviewing challenges in diagnosis and treatment
- PMID: 37600808
- PMCID: PMC10432830
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1208567
Activated PI3Kδ syndrome - reviewing challenges in diagnosis and treatment
Abstract
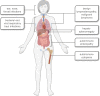
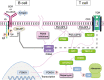
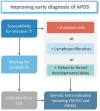
Activated PI3Kδ syndrome (APDS) is a rare inborn error of immunity (IEI) characterized primarily by frequent infections, lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity. Since its initial description in 2013, APDS has become part of the growing group of nearly 500 IEIs affecting various components of the immune system. The two subtypes of APDS - APDS1 and APDS2 - are caused by variants in the PIK3CD and PIK3R1 genes, respectively. Due to the rarity of the disease and the heterogeneous clinical picture, many patients are not diagnosed until years after symptom onset. Another challenge is the large number of PIK3CD and PIK3R1 variants whose functional significance for developing APDS is inconclusive. Treatment of APDS has so far been mostly symptom-oriented with immunoglobulin replacement therapy, immunosuppressive therapies and antibiotic or antiviral prophylaxes. Additionally, allogeneic stem cell transplantation as well as new targeted therapies are options targeting the root cause that may improve patients' quality of life and life expectancy. However, the clinical course of the disease is difficult to predict which complicates the choice of appropriate therapies. This review article discusses diagnostic procedures and current and future treatment options, and highlights the difficulties that physicians, patients and their caretakers face in managing this complex disease. This article is based on cohort studies, the German and US guidelines on the management of primary immunodeficiencies as well as on published experience with diagnosis and compiled treatment experience for APDS.
Keywords: APDS; IEI; PID; inborn errors of immunity; primary immunodeficiency; rare disease; stem cell transplantation; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2023 Vanselow, Wahn and Schuetz.
Conflict of interest statement
Author SV was employed by Infill Healthcare Communication. Author VW received a honorarium from Pharming Group N.V. for the supervision of the writing of this article. His homepage www.immundefekt.de is supported by CSL Behring. Author CS has declined a honorarium for her contribution to this manuscript. She was PI for Phase 3 Study CCDZ173X2201 Novartis and PI for the open extension study CCDZ173X2201E1 Novartis/Pharming. The authors declare that this study received funding from Pharming Group N.V.. The funder had the following involvement in the study: writing of the article.
Figures

References
-
- Tangye SG, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Cunningham-Rundles C, Franco JL, Holland SM, et al. . Human inborn errors of immunity: 2022 update on the classification from the international union of immunological societies expert committee. Springer US (2022) 42(7):1473–507. doi: 10.1007/s10875-022-01289-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

