Serum calprotectin as a marker of neonatal sepsis: a hospital-based cross-sectional diagnostic study
- PMID: 37600908
- PMCID: PMC10432886
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.132099.2
Serum calprotectin as a marker of neonatal sepsis: a hospital-based cross-sectional diagnostic study
Abstract
Background: Despite significant advances in neonatal care, neonatal sepsis remains a major contributor to mortality, morbidity, and protracted hospitalization. The development of early possible diagnostic indicators for newborn sepsis is critical. Since calprotectin participates in major biological processes, it could be a diagnostic marker for infection/inflammation. This study aimed to estimate serum calprotectin in neonates with clinical sepsis. In addition, we compared serum calprotectin with standard sepsis markers and serum procalcitonin to evaluate its diagnostic accuracy.
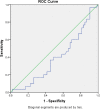
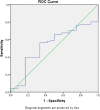
Methods: A hospital-based cross-sectional diagnostic study of neonates identified with clinical sepsis using standard criteria was carried out. We compared estimated serum calprotectin levels to serum procalcitonin levels and conventional sepsis markers (leucocyte count, blood culture, immature to total neutrophil ratio, and C- reactive protein). We used SPSS version 25 to analyze the data. To examine diagnostic accuracy and determine a cut-off value for serum calprotectin, we used the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve.
Results: Of the 83 subjects included, 36.5% (30/83) had blood culture positive status, the median value of serum calprotectin being 0.93 ng/ml (0.67 to 1.3). Respiratory, cardiovascular, and gastrointestinal instabilities were present in 67.5% (56/83), 59% (49/83), and 50.1% (42/83) cases, respectively. The median values of serum calprotectin, procalcitonin, TLC, and I/T ratio between neonates withpositive blood culturesand negative culturesdid not differ significantly.. On ROC, calprotectin was not predictive for blood culture positivity (sensitivity: 50%; specificity: 44% at 0.83 ng/ml of serum calprotectin) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (sensitivity: 57%; specificity: 67% at serum calprotectin levels of 0.89 ng/ml). However, compared with serum procalcitonin, serum calprotectin at 1.2 ng/ml had sensitivity and specificity of 60% and 73%, respectively.
Conclusions: Serum calprotectin did not show a distinct advantage over the existing sepsis markers. Serum calprotectin level at 1.2 ng/ml had a sensitivity and specificity of 60% and 73%, respectively, compared to serum procalcitonin in detecting neonatal sepsis.
Keywords: Calprotectin; Procalcitonin; ROC curve; biomarkers; blood culture; neonatal sepsis; newborn; sepsis.
Copyright: © 2023 Ramineni P et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Serum C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and lactate dehydrogenase for the diagnosis of pancreatic necrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 21;4(4):CD012645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012645. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28431197 Free PMC article.
-
Blood biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 1;2016(5):CD012179. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012179. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27132058 Free PMC article.
-
Serum and urine nucleic acid screening tests for BK polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in kidney and kidney-pancreas transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 28;11(11):CD014839. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014839.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39606952
-
Accuracy of routine laboratory tests to predict mortality and deterioration to severe or critical COVID-19 in people with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 6;8(8):CD015050. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015050.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39105481 Free PMC article.
-
123I-MIBG scintigraphy and 18F-FDG-PET imaging for diagnosing neuroblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 29;2015(9):CD009263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009263.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26417712 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-6 (IL-6) as a significant biomarker in late-onset neonatal sepsis: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 Sep 2;184(9):587. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06409-w. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40892314 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of Serum Calprotectin Relative to Other Biomarkers of Infection in Febrile Infants Presenting to the Emergency Department.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 May 7;13(5):425. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13050425. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786153 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Diagnostic Significance of Calprotectin in Serous Ovarian Carcinoma.Life (Basel). 2025 Jul 8;15(7):1080. doi: 10.3390/life15071080. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724582 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

