Mechanisms of alkaliptosis
- PMID: 37601110
- PMCID: PMC10436304
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1213995
Mechanisms of alkaliptosis
Abstract
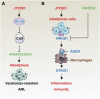
Malignant tumors represent a major threat to global health and the search for effective treatments is imperative. While various treatments exist, including surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy and combination therapies, there remains a need to develop therapies that target regulated cell death pathways to eliminate cancer cells while preserving normal cells. Alkaliptosis, a pH-dependent cell death process triggered by the small molecular compound JTC801, has been identified as a novel approach for malignant tumor treatment, particularly in pancreatic cancer. Two major signaling pathways, the NF-κB-CA9 pathway and the ATP6V0D1-STAT3 pathway, contribute to the induction of alkaliptosis. This review summarizes recent developments in our understanding of alkaliptosis signals, mechanisms, and modulation, and explores its context-dependent effects on drug resistance, inflammation, and immunity. By providing a deeper understanding of the heterogeneity and plasticity of cell death mechanisms, this information holds promise for informing the design of more effective anti-tumor therapies.
Keywords: alkaliptosis; cancer; cell death; immunity; pH.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Kang, Liu and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cappellesso F., Orban M. P., Shirgaonkar N., Berardi E., Serneels J., Neveu M. A., et al. (2022). Targeting the bicarbonate transporter SLC4A4 overcomes immunosuppression and immunotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer. Nat. cancer 3 (12), 1464–1483. 10.1038/s43018-022-00470-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

