Recognising the deterioration of patients in acute care wards: a qualitative study
- PMID: 37601318
- PMCID: PMC10435917
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.17624.2
Recognising the deterioration of patients in acute care wards: a qualitative study
Abstract
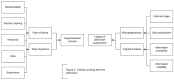
Background: Infrastructure, equipment and staff constraints are often cited as barriers to the recognition and rescue of deteriorating patients in resource-limited settings. The impact of health-system organisation, decision-making and organisational culture on recognition of deterioration is however poorly understood. This study explores how health care providers recognise deterioration of patients in acute care in Sri Lanka. Methods: In-depth interviews exploring decision making and care processes related to recognition of deterioration, were conducted with a purposive sample of 23 health care workers recruited from ten wards at a district hospital in Sri Lanka. Interviews were audio-recorded, transcribed and coded thematically, line-by-line, using a general inductive approach. Results: A legacy of initial assessment on admission and inimical organisational culture undermined recognition of deteriorating patients in hospital. Informal triaging at the time of ward admission resulted in patients presenting with red-flag diagnoses and vital sign derangement requiring resuscitation being categorised as "bad". The legacy of this categorisation was a series of decision-making biases anchored in the initial assessment, which remained with the patient throughout their stay. Management for patients categorised as "bad" was prioritised by healthcare workers coupled with a sense of fatalism regarding adverse outcomes. Health care workers were reluctant to deviate from the original plan of care despite changes in patient condition (continuation bias). Organisational culture - vertical hierarchy, siloed working and a reluctance to accept responsibility- resulted in omissions which undermined recognition of deterioration. Fear of blame was a barrier to learning from adverse events. Conclusions: The legacy of admission assessment and hospital organisational culture undermined recognition of deterioration. Opportunities for improving recognition of deterioration in this setting may include establishing formal triage and medical emergency teams to facilitate timely recognition and escalation.
Keywords: Critical care; Recognition of deterioration.
Copyright: © 2022 Beane A et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials