Immunogenicity of BNT162b2 in children 6 months to under 5 years of age with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection, in the era of Omicron predominance
- PMID: 37601322
- PMCID: PMC10432840
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2023.100367
Immunogenicity of BNT162b2 in children 6 months to under 5 years of age with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection, in the era of Omicron predominance
Abstract
Background: Children 6 months to < 5 years old are recommended to receive 3-dose regimen of BNT162b2. Children previously infected with Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 develop immunity from natural infection, therefore may require fewer doses of vaccine.
Objective: To compare immunogenicity of 1- or 2-dose BNT162b2 in healthy children post COVID-19 with 3-dose BNT162b2 in COVID-naïve children.
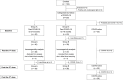
Methods: Children aged 6 months to < 5 years who developed COVID-19 during the Omicron-predominant period were enrolled; Group A 3-6 months(N = 40) and Group B > 6 months(N = 40) prior to vaccination. Participants in Group A and B received 2-dose BNT162b2 intramuscularly 1 month apart. COVID-naïve children were enrolled as a control group (N = 40) and received 3-dose BNT162b2 at month 0,1,3. Neutralizing antibody against Omicron variant(BA.2.75 and BA.4/5) was determined by pseudovirus assays(pVNT) as reported by neutralization dilution for 50%inhibition (ID50) at 28 days after the 1st and 2nd dose.
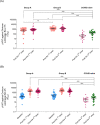
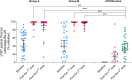
Results: From October-November 2022, 120 children with a median age of 2.8 years (IQR 1.6-4.0) were enrolled. The median duration since COVID-19 to vaccination was 4.4 months(IQR 3.8-5.4) in Group A and 7.9 months(7.0-8.5) in Group B. In Group A, the geometric means(GMs) of pVNT-BA.2.75 ID50 were 553 (95%CI 338-906) and 753(516-1098) after 1 and 2 doses, respectively, and the GMs of pVNT-BA.4/5 ID50 were 1936(1402-2673) and 1885(1414-2512), respectively. In Group B, the GMs of pVNT-BA.2.75 ID50 were 1383(1100-1742) and 1419 (1104-1823), and the GMs of pVNT-BA.4/5 ID50 were 2627(2048-3367) and 2056(1546-2735), respectively. Meanwhile in COVID-naïve group, the GMs of pVNT-BA.2.75 and pVNT-BA.4/5 ID50 were 158(98-255) and 59(31-114) after the 3rd dose, respectively. The geometric mean ratio(GMR) of pVNT-BA.2.75 ID50 after 1 dose in Group A and B compared with after 3 doses in COVID-naïve group were 3.50 (1.93-6.34) and 8.74 (4.79-15.95), respectively. The GMR of pVNT-BA.2.75 ID50 after 1 dose in Group B compared with Group A was 2.50 (1.45-4.31).
Conclusions: Children previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, developed robust neutralizing antibody response against Omicron variant after single-dose BNT162b2. Children with an interval of > 6 months since COVID-19 infection developed higher neutralizing antibody response compared to those with a 3-to-6-month interval.
Keywords: Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG; BNT162b2 vaccine; Child; Infant; Neutralizing antibody titer; SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern 2021 [Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1..... Accessed date February 26, 2023.
-
- GISAID. Tracking of hCoV-19 Variants [Available from: https://gisaid.org/hcov19-variants/. Accessed date February 26, 2023.
-
- Hodcroft EB. CoVariants: SARS-CoV-2 Mutations and Variants of Interest 2023 [Available from: https://covariants.org/. Accessed date February 26, 2023.
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association. Children and COVID-19: State-Level Data Report 2023 [Available from: https://www.aap.org/en/pages/2019-novel-coronavirus-covid-19-infections/.... Accessed date 5 March, 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

