MALAT1 in Liquid Biopsy: The Diagnostic and Prognostic Promise for Colorectal Cancer and Adenomas?
- PMID: 37601809
- PMCID: PMC10439781
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S420127
MALAT1 in Liquid Biopsy: The Diagnostic and Prognostic Promise for Colorectal Cancer and Adenomas?
Abstract
Introduction: The development of colorectal cancer (CRC) is a multistep process accompanied by the accumulation of mutations that start from specific precancerous lesion - colorectal adenomas (CA). CRC incidence and mortality can be reduced by the early identification of these neoplasm. Colonoscopy is the most widely used screening method for CRC identification. Nowadays, clinical research interest is shifting to the use of liquid biopsy that may help with the early diagnosis of CA and CRC. In our previous study, we identified long non-coding RNA MALAT1 gene amplification associated with the development of CA.
Methods: This study aimed to describe the potential of MALAT1 expression levels in the adenoma tissue of patients used in the previous study by real-time qPCR. Furthermore, we analysed the plasma samples of an independent group of patients with CA (n=97), CRC (n=101), and cancer-free individuals (CFI, n=48).
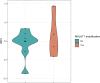
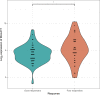
Results: There was no difference in the MALAT1 expression level between CA patients with or without MALAT1 amplification. However, the plasma MALAT1 expression levels were significantly upregulated in patients with CRC and CA compared to CFI (for both p<0.001). Moreover, a correlation between MALAT1 expression and histological types of adenomas was identified- high-CRC-risk adenomas also displayed the highest MALAT1 expression levels. Furthermore, in CRC patients, MALAT1 levels were associated with a response to therapy.
Conclusion: MALAT1 expression levels could serve as a promising circulating biomarker for early CA and CRC diagnosis, and even as a predictor of therapy response in CRC patients.
Keywords: MALAT1; colorectal adenomas; colorectal cancer; liquid biopsy; plasma.
© 2023 Cervena et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Discovery of Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 Amplification in Precancerous Colorectal Lesions.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 11;23(14):7656. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147656. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887000 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of lncRNA MALAT1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 May 15;7(6):3174-81. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25031737 Free PMC article.
-
Association of lncRNA-p53 regulatory network (lincRNA-p21, lincRNA-ROR and MALAT1) and p53 with the clinicopathological features of colorectal primary lesions and tumors.Oncol Lett. 2020 Jun;19(6):3937-3949. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11518. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32391102 Free PMC article.
-
MALAT1 in colorectal cancer: Its implication as a diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarker.Gene. 2022 Nov 15;843:146791. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146791. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35961438 Review.
-
Colorectal Adenomas-Genetics and Searching for New Molecular Screening Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 5;21(9):3260. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093260. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32380676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

