Identification and interpretation of TET2 noncanonical splicing site intronic variants in myeloid neoplasm patients
- PMID: 37601840
- PMCID: PMC10435687
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.744
Identification and interpretation of TET2 noncanonical splicing site intronic variants in myeloid neoplasm patients
Abstract
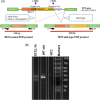
Background: DNA hypermethylation and instability due to inactivation mutations in Ten-eleven translocation 2 (TET2) is a key biomarker of hematological malignancies. This study aims at characterizing two intronic noncanonical splice-site variants, c.3954+5_3954+8delGTTT and c.3954+5G>A. Methods: We used in silico prediction tools, reverse transcription (RT)-PCR, and Sanger sequencing on blood/bone marrow-derived RNA specimens to determine the aberrant splicing. Results: In silico prediction of both variants exhibited reduced splicing strength at the TET2 intron 7 splicing donor site. RT-PCR and Sanger sequencing identified a 62-bp deletion at the exon 7, producing a frameshift mutation, p.Cys1298*. Conclusion: This study provides functional evidence for two intronic TET2 variants that cause alternative splicing and frameshift mutation.
Keywords: TET2; in silico prediction; myeloid neoplasm; next‐generation sequencing (NGS); noncanonical splicing site; ten‐eleven translocation 2; tumor suppressor.
© 2023 The Authors. eJHaem published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures


References
-
- Delhommeau F, Dupont S, Della Valle V, James C, Trannoy S, Masse A, et al. Mutation in TET2 in myeloid cancers. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(22):2289–301. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
