Levels of inflammatory markers are differentially expressed in sickle cell anemia and sickle cell trait
- PMID: 37601842
- PMCID: PMC10435695
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.712
Levels of inflammatory markers are differentially expressed in sickle cell anemia and sickle cell trait
Abstract
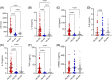
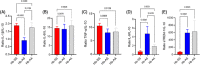
Although sickle cell anemia (SCA) is related to inflammation, the profile of inflammatory markers in sickle cell trait (SCT) is poorly studied. This is a cross-sectional study of inflammatory biomarkers carried out involving adults with SCA in steady state, SCT and controls. The SCA group had higher levels of lactato dehydrogenase, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor alpha than the others, while the SCT group had similar levels to control group. In addition, SCA group had lower IL-8/IL-10 and soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1/IL-10 ratios. These findings indicate that individuals with SCT do not have a chronic inflammatory profile and reinforce that cytokines are involved in the maintenance of the inflammatory state in SCA.
Keywords: adults; cytokines; inflammation; sickle cell anemia; sickle cell trait.
© 2023 The Authors. eJHaem published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Conran N, Franco‐Penteado CF, Costa FF. Newer aspects of the pathophysiology of sickle cell disease vaso‐occlusion. Hemoglobin. 2009;33(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Connes P, Reid H, Hardy‐Dessources MD, Morrison E, Hue O. Physiological responses of sickle cell trait carriers during exercise. Sports Med. 2008;38(11):931–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
