Vidjil add-on for MRD quantification of samples processed using the EuroClonality-NGS protocol
- PMID: 37601854
- PMCID: PMC10435716
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.749
Vidjil add-on for MRD quantification of samples processed using the EuroClonality-NGS protocol
Abstract
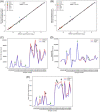
Assessment of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by immune repertoire NGS requires spiking CDR3 sequences at known quantities into the patient's sample. Recently, the EuroClonality-NGS group released one of the most comprehensive protocols for this purpose. ARResT/Interrogate is a closed-source software for processing these NGS libraries, developed by this same group. Vidjil, an open-source alternative, currently cannot handle libraries prepared using this protocol. Here, we present a Vidjil add-on to solve this issue. EuroClonality-NGS prepared samples analyzed with Vidjil and ARResT/Interrogate were highly concordant (r = 0.998) and presented low error (root-mean-square error, RMSE = 0.112).
Keywords: T‐cell receptor; Vidjil; immune repertoire; immunoglobulin genes; leukemia; minimal residual disease.
© 2023 The Authors. eJHaem published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The institution Centro Infantil Boldrini is a part of the VidjilNet Consortium. Florian Thonier is a developer in the Vidjil team.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Standardized next-generation sequencing of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations for MRD marker identification in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia; a EuroClonality-NGS validation study.Leukemia. 2019 Sep;33(9):2241-2253. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0496-7. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Leukemia. 2019. PMID: 31243313 Free PMC article.
-
Is Next-Generation Sequencing the way to go for Residual Disease Monitoring in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia?Mol Diagn Ther. 2017 Oct;21(5):481-492. doi: 10.1007/s40291-017-0277-9. Mol Diagn Ther. 2017. PMID: 28452038 Review.
-
One-Step Next-Generation Sequencing of Immunoglobulin and T-Cell Receptor Gene Recombinations for MRD Marker Identification in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2453:43-59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2115-8_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35622319 Free PMC article.
-
Quality control and quantification in IG/TR next-generation sequencing marker identification: protocols and bioinformatic functionalities by EuroClonality-NGS.Leukemia. 2019 Sep;33(9):2254-2265. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0499-4. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Leukemia. 2019. PMID: 31227779 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Gene Rearrangements: Unique Signatures for Tracing Physiological Lymphocytes and Leukemic Cells.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jun 27;12(7):979. doi: 10.3390/genes12070979. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34198966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Dongen JJM, Seriu T, Panzer‐Grümayer ER, Biondi A, Pongers‐Willemse MJ, Corral L, et al. Prognostic value of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in childhood. Lancet. 1998;352(9142):1731–8. - PubMed
-
- van der Velden VHJ, Hochhaus A, Cazzaniga G, Szczepanski T, Gabert J, van Dongen JJM. Detection of minimal residual diseasein hematologic malignancies by real‐time quantitative PCR: principles, approaches, and laboratory aspects. Leukemia. 2003;17(6):1013–34. - PubMed
-
- Tran TH, Hunger SP. The genomic landscape of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and precision medicine opportunities. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;84:144–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
