Real-world complication burden and disease management paradigms in transfusion-related β-thalassaemia in Greece: Results from ULYSSES, an epidemiological, multicentre, retrospective cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37601860
- PMCID: PMC10435690
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.695
Real-world complication burden and disease management paradigms in transfusion-related β-thalassaemia in Greece: Results from ULYSSES, an epidemiological, multicentre, retrospective cross-sectional study
Abstract
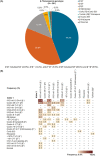
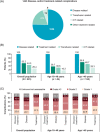
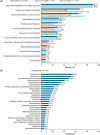
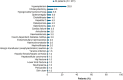
Patients with transfusion-dependent beta (β)-thalassaemia experience a broad range of complications. ULYSSES, an epidemiological, multicentre, retrospective cross-sectional study, aimed to assess the prevalence and severity of treatment and disease complications, capture disease management and identify predictors of complications in patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia, treated in routine settings in Greece. Eligible patients were adults diagnosed with β-thalassaemia ≥12 months before enrolment and having received ≥6 red blood cell (RBC) units (excluding elective surgery) with no transfusion-free period ≥35 days in the 24 weeks before enrolment. Primary data were collected at a single visit and through chart review. Between Oct 21, 2019, and Jun 15, 2020, 201 eligible patients [median (interquartile range, IQR) age 45.7 (40.2-50.5) years; 75.6% > 40 years old; 64.2% female] were enrolled, a mean (standard deviation) of 42.9 (7.8) years after diagnosis. Median (IQR) age at diagnosis and RBC transfusion initiation were 0.8 (0.4-2.8) and 1.3 (1.0-5.0) years, respectively. From diagnosis to enrolment, patients had developed a median of six (range: 1-55) complications; 19.6% were grade ≥3. The most represented complications were endocrine/metabolic/nutrition disorders (91.5%), surgical/medical procedures (67.7%) and blood/lymphatic system disorders (64.7%). Real-world data generated by ULYSSES underscore the substantial complication burden of transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia patients, routinely managed in Greece.
Keywords: complications; epidemiological; real‐world; transfusion‐related β‐thalassaemia.
© 2023 The Authors. eJHaem published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Antonis Kattamis has received grants from Novartis and Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene; consulting fees from Agios Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Crispr/Vertex, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Novartis and Vifor; honoraria from Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Chiesi and Crispr/Vertex; and meeting/travel support from Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene.Sophia Delicou has received consulting fees, honoraria and meeting/travel support from Novartis and Bristol Myers Squibb.Foteini Petropoulou has received grants and/or study funding from Genesis Pharma, Protagonist Therapeutics and Celgene; consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb; and has attended advisory board meetings for Bristol Myers Squibb.Michael D. Diamantidis has received study funding/grants from Genesis Pharma, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Forma Therapeutics Inc., Synteract and Vifor International Inc.; honoraria from Genesis Pharma, Uni‐Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb and Abbvie; meeting/travel support from Demo Company, Bristol Myers Squibb and Genesis Pharma; and has attended advisory board meetings for Bristol Myers Squibb.Loukia Evliati has received study funding from Genesis Pharma.Panagiotis Viktoratos is an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb.Alexandra Kourakli has received study funding/grants from Bristol Myers Squibb; consulting fees from Forma Therapeutics Inc.; honoraria from Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb and Elpen; meeting/travel support from Glaxo and Rafarm; and has attended advisory board meetings for Genesis, Gilead and Agios.Ersi Voskaridou, Evangelos Klironomos, Ioannis Lafiatis, Stylianos Lafioniatis, Eleni Kapsali, Kiki Karvounis‐Marolachakis, Despoina Timotheatou and Chrysoula Deligianni have no disclosures to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Luspatercept for the treatment of anaemia in non-transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia (BEYOND): a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet Haematol. 2022 Oct;9(10):e733-e744. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(22)00208-3. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Lancet Haematol. 2022. PMID: 36007538 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of mitapivat, an oral pyruvate kinase activator, in adults with non-transfusion dependent α-thalassaemia or β-thalassaemia: an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study.Lancet. 2022 Aug 13;400(10351):493-501. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01337-X. Lancet. 2022. PMID: 35964609 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical and health-related quality of life outcomes of transfusion-dependent thalassaemia patients in Singapore.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2021 May;88:102547. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2021.102547. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2021. PMID: 33607590
-
Extramedullary haematopoiesis in patients with transfusion dependent β-thalassaemia (TDT): a systematic review.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):764-774. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2048065. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 35261317 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Literature Review of the Burden of Disease and Treatment for Transfusion-dependent β-Thalassemia.Clin Ther. 2020 Feb;42(2):322-337.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.12.003. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Clin Ther. 2020. PMID: 31882227
Cited by
-
Addressing Thalassaemia Management from Patients' Perspectives: An International Collaborative Assessment.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Apr 18;60(4):650. doi: 10.3390/medicina60040650. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38674296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kattamis A, Kwiatkowski JL, Aydinok Y. Thalassaemia. Lancet. 2022;399(10343):2310–24. - PubMed
-
- Taher AT, Musallam KM, Cappellini MD. β‐Thalassemias. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):727–43. - PubMed
-
- Cappellini MD, Porter JB, Viprakasit V, Taher AT. A paradigm shift on beta‐thalassaemia treatment: how will we manage this old disease with new therapies? Blood Rev. 2018;32(4):300–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
