In vivo exposure to bisphenol F induces oxidative testicular toxicity: role of Erβ and p53/Bcl-2 signaling pathway
- PMID: 37601897
- PMCID: PMC10433915
- DOI: 10.3389/frph.2023.1204728
In vivo exposure to bisphenol F induces oxidative testicular toxicity: role of Erβ and p53/Bcl-2 signaling pathway
Abstract
Introduction: Bisphenol F (BPF), an alternative to bisphenol A has been implicated as a gonadotoxic substance. BPF has been shown to induce hormonal imbalance and testicular oxidative damage. However, the mechanism associated with BPF-induced testicular toxicity has not been fully explored. This study was designed to explore the role of tumor protein (p53)/ B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCl-2) signaling and oestrogen receptor beta (Erβ) in BPF-induced testicular toxicity.
Methods: Male Wistar rats were randomized into control (Cntrl), BPF-treated (10, 30, and 50 mg/kg for low dose (BPF-L), medium dose (BPF-M), and high dose (BPF-H) respectively), and BPF-treated recovery (Cntrl-R, BPF-L-R, BPF-M-R, and BPF-H-R). The administration was via gavage and lasted for 28 days and the animals in the recovery groups were allowed 28-days exposure free period for recovery from BPF exposure.
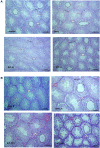
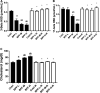
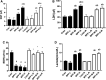
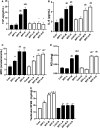
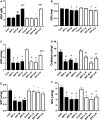
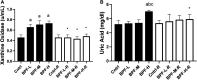
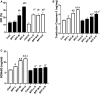
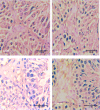
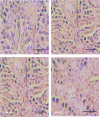
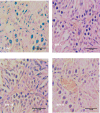
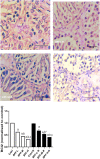
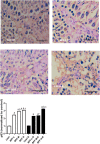
Results: BPF resulted in the distortion of the testicular histoarchitecture, which was accompanied by a significant rise in testicular gamma-lutamyl transferase and lactate dehydrogenase activities but a decline in sorbitol dehydrogenase activities. Also, BPF caused a significant reduction in plasma gonadotropin-releasing hormone, luteinising hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and testosterone, which was associated with the downregulation of testicular 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities. Furthermore, BPF induced testicular inflammation, redox imbalance, and apoptosis, accompanied by distortion in p53/BCl-2 signaling and overexpression of Erβ. Again, the observed toxic effects of BPF were dose-dependent and not completely reversed by BPF cessation.
Discussion: Bisphenol F induced gonadotoxicity by distorting p53/BCl2 signaling and the expression of Erβ. These observed alterations were not completely reversed after the cessation of BPF exposure.
Keywords: apoptosis; bisphenol f; endocrine disruptors; hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis; inflammation; oxidative stress.
© 2023 Odetayo, Adeyemi, and Olayaki.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Omega 3 fatty acid improves sexual and erectile function in BPF-treated rats by upregulating NO/cGMP signaling and steroidogenic enzymes activities.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 23;13(1):18060. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45344-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37872365 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 fatty acid ameliorates bisphenol F-induced testicular toxicity by modulating Nrf2/NFkB pathway and apoptotic signaling.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 20;14:1256154. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1256154. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37800144 Free PMC article.
-
Omega 3 fatty acids preserve testicular function by ameliorating BPF-induced dysthyroidism: role of p53/Bcl-2 signaling and proton pump activities.JBRA Assist Reprod. 2024 Aug 26;28(3):471-482. doi: 10.5935/1518-0557.20240033. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2024. PMID: 38801312 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of bisphenol F on sexual performance and quality of offspring in Male Wistar rats.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 Oct 1;244:114079. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114079. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022. PMID: 36115153
-
A new chapter in the bisphenol A story: bisphenol S and bisphenol F are not safe alternatives to this compound.Fertil Steril. 2015 Jan;103(1):11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.11.005. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Fertil Steril. 2015. PMID: 25475787 Review.
Cited by
-
Omega 3 fatty acid improves sexual and erectile function in BPF-treated rats by upregulating NO/cGMP signaling and steroidogenic enzymes activities.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 23;13(1):18060. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45344-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37872365 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Toxicity Induced by Bisphenol F in Labeo rohita Fish Using Multiple Biomarker Approach.Scientifica (Cairo). 2024 Nov 8;2024:8646751. doi: 10.1155/2024/8646751. eCollection 2024. Scientifica (Cairo). 2024. PMID: 39555222 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Therapy with Vitamin D and Metformin: A Potential Approach to Mitigate Testicular Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Reprod Sci. 2024 Dec;31(12):3795-3807. doi: 10.1007/s43032-024-01708-3. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Reprod Sci. 2024. PMID: 39317887
-
Omega-3 fatty acid ameliorates bisphenol F-induced testicular toxicity by modulating Nrf2/NFkB pathway and apoptotic signaling.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 20;14:1256154. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1256154. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37800144 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic role of omega 3 fatty acids in bisphenol F-induced sexual and erectile dysfunction is associated with penile redox homeostasis.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jun 23;43:102103. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102103. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40641745 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

