Synergistic graphene-MnOx/honeycomb activated carbon (G-MnOx/HAC) and plasma technology for eradication of pathogenic microorganisms
- PMID: 37601903
- PMCID: PMC10433192
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1207947
Synergistic graphene-MnOx/honeycomb activated carbon (G-MnOx/HAC) and plasma technology for eradication of pathogenic microorganisms
Abstract
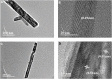
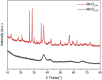
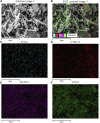
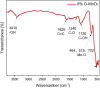
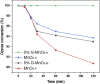
This paper addresses the risk for environmental transmission of pathogenic microorganisms in confined spaces and the serious health hazards for personnel, and research on efficient eradication methods for the pathogenic microorganisms was carried out to provide technical support for ensuring the health of personnel in confined spaces. A series of graphene-MnO2 (G-MnO2) catalytic materials was prepared by hydrothermal and precipitation methods, and processing parameters such as the graphene doping method, the raw material ratio and the plasma action time were optimized. It was shown that G-MnOX-P/HAC prepared by a one-step precipitation method and with a graphene doping ratio of 10% had the best bactericidal effect in a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) reactor after 4 min of reaction. The eradication rates for Escherichia coli (E. coli), Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), coronavirus and Aspergillus niger were all greater than 99.9%. The characterization techniques TEM, SEM, XRD, XPS, BET and FT-IR showed that the G-MnOX-P samples prepared by the one-step precipitation method had larger specific surface areas with more oxygen vacancies and functional groups on the surfaces, which was conducive to decomposition of the ozone generated by the dissociated plasma and formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) for the microbial eradication process. Finally, by comparing the ozone-decomposition activity with the plasma co-catalytic performance, it was verified that efficient decomposition of the ozone facilitated the eradication of microorganisms. Based on this, an analysis of the mechanism for efficient eradication was carried out.
Keywords: DBD plasma; G-MnOX-P/HAC; confined space; eradication; pathogenic microorganisms.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Jia, Lv, Xiong, Su, Huang and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Aziz K. H., Miessner H., Mueller S., Mahyar A., Kalass D., Moeller D., et al. (2018). Comparative study on 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2, 4-dichlorophenol removal from aqueous solutions via ozonation, photocatalysis and non-thermal plasma using a planar falling film reactor. J. Hazard. Mat. 343 (5), 107–115. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.025 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ben B. Z., Carrã G., Charpentier E., Le-Bras F., Maho T., Robert E., et al. (2017). Innovative non-thermal plasma disinfection process inside sealed bags: Assessment of bactericidal and sporicidal effectiveness in regard to current sterilization norms. PLoS ONE 12 (6), e0180183. 10.1371/journal.pone.0180183 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger C., Song Z. M., Li T. B., Ogbazghi A. Y., Feng R. (2004). Ultrathin epitaxial Graphite: 2D electron gas properties and a route toward graphene-based nanoelectronics. J. Phys. Chem. 108 (52), 19912–19916. 10.1021/jp040650f - DOI
-
- Brągoszewska E., Bogacka M., Pikoń K. (2020). Effectiveness and eco-costs of air cleaners in terms of improving fungal air pollution in dwellings located in southern Poland-A preliminary study. Atmosphere 11 (11), 1255. 10.3390/atmos11111255 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

