Biofabrication of novel silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles from Fusarium solani IOR 825 and their potential application in agriculture as biocontrol agents of phytopathogens, and seed germination and seedling growth promoters
- PMID: 37601908
- PMCID: PMC10436318
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1235437
Biofabrication of novel silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles from Fusarium solani IOR 825 and their potential application in agriculture as biocontrol agents of phytopathogens, and seed germination and seedling growth promoters
Abstract
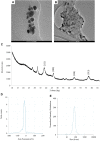
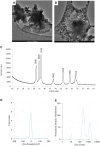
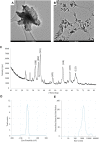
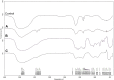
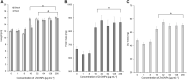
Introduction: Plant pathogenic microorganisms adversely affect the growth and yield of crops, which consequently leads to losses in food production. Metal-based nanoparticles (MNPs) can be a remedy to solve this problem. Methods: Novel silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) were biosynthesized from Fusarium solani IOR 825 and characterized using Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and measurement of Zeta potential. Antibacterial activity of NPs was evaluated against four plant pathogenic strains by determination of the minimum inhibitory (MIC) and biocidal concentrations (MBC). Micro-broth dilution method and poisoned food technique were used to assess antifungal activity of NPs against a set of plant pathogens. Effect of nanopriming with both types of MNPs on maize seed germination and seedlings growth was evaluated at a concentration range of 1-256 μg mL-1. Results: Mycosynthesis of MNPs provided small (8.27 nm), spherical and stable (zeta potential of -17.08 mV) AgNPs with good crystallinity. Similarly, ZnONPs synthesized by using two different methods (ZnONPs(1) and ZnONPs(2)) were larger in size (117.79 and 175.12 nm, respectively) with Zeta potential at -9.39 and -21.81 mV, respectively. The FTIR spectra showed the functional groups (hydroxyl, amino, and carboxyl) of the capping molecules on the surface of MNPs. The values of MIC and MBC of AgNPs against bacteria ranged from 8 to 256 μg mL-1 and from 512 to 1024 μg mL-1, respectively. Both types of ZnONPs displayed antibacterial activity at 256-1024 μg mL-1 (MIC) and 512-2048 μg mL-1 (MBC), but in the concentration range tested, they revealed no activity against Pectobacterium carotovorum. Moreover, AgNPs and ZnONPs inhibited the mycelial growth of Alternaria alternata, Fusarium culmorum, Fusarium oxysporum, Phoma lingam, and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. MIC and MFC values of AgNPs ranged from 16-128 and 16-2048 μg mL -1, respectively. ZnONPs showed antifungal activity with MIC and MFC values of 128-2048 μg mL-1 and 256-2048 μg mL-1, respectively. The AgNPs at a concentration of ≥32 μg mL-1 revealed sterilization effect on maize seeds while ZnONPs demonstrated stimulatory effect on seedlings growth at concentrations of ≥16 μg mL-1 by improving the fresh and dry biomass production by 24% and 18%-19%, respectively. Discussion: AgNPs and ZnONPs mycosynthesized from F. solani IOR 825 could be applied in agriculture to prevent the spread of pathogens. However, further toxicity assays should be performed before field evaluation. In view of the potential of ZnONPs to stimulate plant growth, they could be crucial in increasing crop production from the perspective of current food assurance problems.
Keywords: applied microbiology; biocontrol; biofabrication; biogenic nanoparticles; bionanotechnology; crop protection; mycosynthesis; plant pathogens.
Copyright © 2023 Trzcińska-Wencel, Wypij, Terzyk, Rai and Golińska.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abd El-Aziz A. R. M., Al-Othman M. R., Mahmoud M. A., Metwaly H. A. (2015). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Fusarium solani and its impact on grain borne fungi. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 10, 655–662.
-
- Abdullah F. H., Bakar N. A., Bakar M. A. (2020). Low temperature biosynthesis of crystalline zinc oxide nanoparticles from Musa acuminata peel extract for visible-light degradation of methylene blue. Optik 206, 164279. 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164279 - DOI
-
- Abdul‐Baki A. A., Anderson J. D. (1973). Vigor determination in soybean seed by multiple criteria 1. Crop Sci. 13, 630–633. 10.2135/cropsci1973.0011183X001300060013x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

