Unveiling the antitumor potential of novel N-(substituted-phenyl)-8-methoxycoumarin-3-carboxamides as dual inhibitors of VEGFR2 kinase and cytochrome P450 for targeted treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37601910
- PMCID: PMC10436493
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1231030
Unveiling the antitumor potential of novel N-(substituted-phenyl)-8-methoxycoumarin-3-carboxamides as dual inhibitors of VEGFR2 kinase and cytochrome P450 for targeted treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
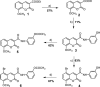
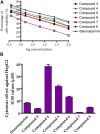
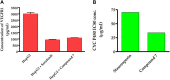
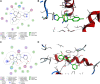
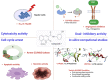
Being the sixth most diagnosed cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, liver cancer is considered as a serious disease with a high prevalence and poor prognosis. Current anticancer drugs for liver cancer have drawbacks, such as limited efficacy in later stages of the disease, toxicity to healthy cells, and the potential for drug resistance. There is ample evidence that coumarin-based compounds are potent anticancer agents, with numerous analogues currently being investigated in preclinical and clinical studies. The current study aimed to explore the antitumor potency of a new class of 8-methoxycoumarin-3-carboxamides against liver cancer. Toward this aim, we have designed, synthesized, and characterized a new set of N-(substituted-phenyl)-8-methoxycoumarin-3-carboxamide analogues. The assessment of antitumor activity revealed that the synthesized class of compounds possesses substantial cytotoxicity toward Hep-G2 cells when compared to staurosporine, without significant impact on normal cells. Out of the synthesized compounds, compound 7 demonstrated the most potent cytotoxic effect against Hep-G2 cells with an IC50 of 0.75 µM, which was more potent than the drug staurosporine (IC50 = 8.37 µM). The investigation into the mechanism behind the antiproliferative activity of compound 7 revealed that it interferes with DNA replication and induces DNA damage, leading to cell cycle arrest as demonstrated by a significant decrease in the percentage of cells in the G1 and G2/M phases, along with an increase in the percentage of cells in the S phase. Flow cytometric analysis further revealed that compound 7 has the ability to trigger programmed cell death by inducing necrosis and apoptosis in HepG-2 cells. Further explorations into the mechanism of action demonstrated that compound 7 displays a potent dual-inhibitory activity toward cytochrome P450 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) proteins, as compared to sorafenib drug. Further, detailed computational studies revealed that compound 7 displays a considerable binding affinity toward the binding cavity of VEGFR2 and CYP450 proteins. Taken together, our findings indicate that the newly synthesized class of compounds, particularly compound 7, could serve as a promising scaffold for the development of highly effective anticancer agents against liver cancer.
Keywords: VEGFR2; apoptosis; cell arrest; coumarin; cytochrome P450; cytotoxicity; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Copyright © 2023 Radwan, Abo-Elabass, Abd El-Baky, Alshwyeh, Almaimani, Almaimani, Ibrahim, Albogami, Jaremko, Alshawwa and Saied.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Novel 8-Methoxycoumarin-3-Carboxamides with potent anticancer activity against liver cancer via targeting caspase-3/7 and β-tubulin polymerization.BMC Chem. 2023 Dec 2;17(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13065-023-01063-5. BMC Chem. 2023. PMID: 38041156 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 1,3-Thiazole Analogues with Potent Activity against Breast Cancer: A Design, Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Silico Study.Molecules. 2022 Jul 31;27(15):4898. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154898. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956848 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, anticancer effect and molecular modeling of new thiazolylpyrazolyl coumarin derivatives targeting VEGFR-2 kinase and inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Apr;85:253-273. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.12.040. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 30641320
-
Novel benzothiazole-based dual VEGFR-2/EGFR inhibitors targeting breast and liver cancers: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity, QSAR and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Feb 15;58:128529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128529. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007724 Review.
-
Evolution of 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)indoline-2-one as a scaffold for potent and selective anticancer activity.RSC Med Chem. 2022 May 9;13(6):711-725. doi: 10.1039/d2md00110a. eCollection 2022 Jun 22. RSC Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35814932 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the multifaceted antiproliferative efficacy of Cichorium endivia root extract by dual modulation of apoptotic and inflammatory genes, inducing cell cycle arrest, and targeting COX-2.RSC Adv. 2024 Jun 17;14(27):19400-19427. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02131b. eCollection 2024 Jun 12. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38887636 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the pharmacological potential of Brennnesselwurzel (Urtica dioica L.): an in-depth study on multifaceted biological activities.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):413. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04709-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39696148 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the therapeutic potential of trimetazidine in rheumatoid arthritis via targeting mi-RNA128a, TLR4 signaling pathway, and adenosine-induced FADD-microvesicular shedding: In vivo and in silico study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 11;15:1406939. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1406939. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38919260 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective thiazole sulfonamides against 6-OHDA-induced Parkinsonian model: in vitro biological and in silico pharmacokinetic assessments.RSC Adv. 2025 Feb 10;15(6):4281-4295. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04941a. eCollection 2025 Feb 6. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 39931414 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and multi-target antiproliferative evaluation of novel 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione analogues against breast cancer: in silico and in vitro mechanistic insights.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 14;15(30):24769-24790. doi: 10.1039/d5ra02512e. eCollection 2025 Jul 10. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40661216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelgalil M. M., Ammar Y. A., Elhag Ali G. A. M., Ali A. Kh., Ragab A. (2023). A novel of quinoxaline derivatives tagged with pyrrolidinyl scaffold as a new class of antimicrobial agents: Design, synthesis, antimicrobial activity, and molecular docking simulation. J. Mol. Struct. 1274, 134443. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134443 - DOI
-
- Alfayomy A. M., Abdel-Aziz S. A., Marzouk A. A., Shaykoon M. S. A., Narumi A., Konno H., et al. (2021). Design and synthesis of pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile hybrids as COX-2 inhibitors: Anti-inflammatory activity, ulcerogenic liability, histopathological and docking studies. Bioorg Chem. 108, 104555. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104555 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alzahrani A. Y., Ammar Y. A., Abu-Elghait M., Salem M. A., Assiri M. A., Ali T. E., et al. (2022). Development of novel indolin-2-one derivative incorporating thiazole moiety as DHFR and quorum sensing inhibitors: Synthesis, antimicrobial, and antibiofilm activities with molecular modelling study. Bioorg Chem. 119, 105571. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105571 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amin K. M., Abou-Seri S. M., Awadallah F. M., Eissa A. A. M., Hassan G. S., Abdulla M. M. (2015). Synthesis and anticancer activity of some 8-substituted-7-methoxy-2H-Chromen-2-One derivatives toward hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 90, 221–231. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.11.027 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

